Buzzers are among the most versatile audio signal devices, commonly used for delivering notifications in cars, phones, kitchen appliances, and more. These low-cost, high-quality audio devices are also compact and easy to integrate with fabricated PCBs, even in space-constrained applications. In this guide, we explore two of the most popular types of buzzers—piezo and magnetic—to help you choose the best option for your project. Read on to learn more!
Contents
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Definition
- Piezo Buzzer
- Magnetic Buzzer
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Characteristics
- Piezo Buzzer
- Magnetic Buzzer
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Structure
- Piezo Buzzer
- Magnetic Buzzer
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Working Principle
- Piezo Buzzer
- Magnetic Buzzer
- Variants of Buzzers
- Electromagnetic Buzzers
- Mechanical Buzzers
- Electromechanical Buzzers
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Transducers and Indicators
- Key Specifications of Buzzers
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Frequency Response
- Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
- Resonant Frequency
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Operating Voltage
- Impedance
- Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Applications
- Summary
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Definition
There are five common buzzer types, but piezo and magnetic buzzers dominate the market.
Piezo Buzzer
A piezo buzzer uses the piezoelectric phenomenon to produce sound when a voltage goes through the ceramic piezoelectric element. Its structure consists of two metal conductors that sandwich a piezoceramic layer.
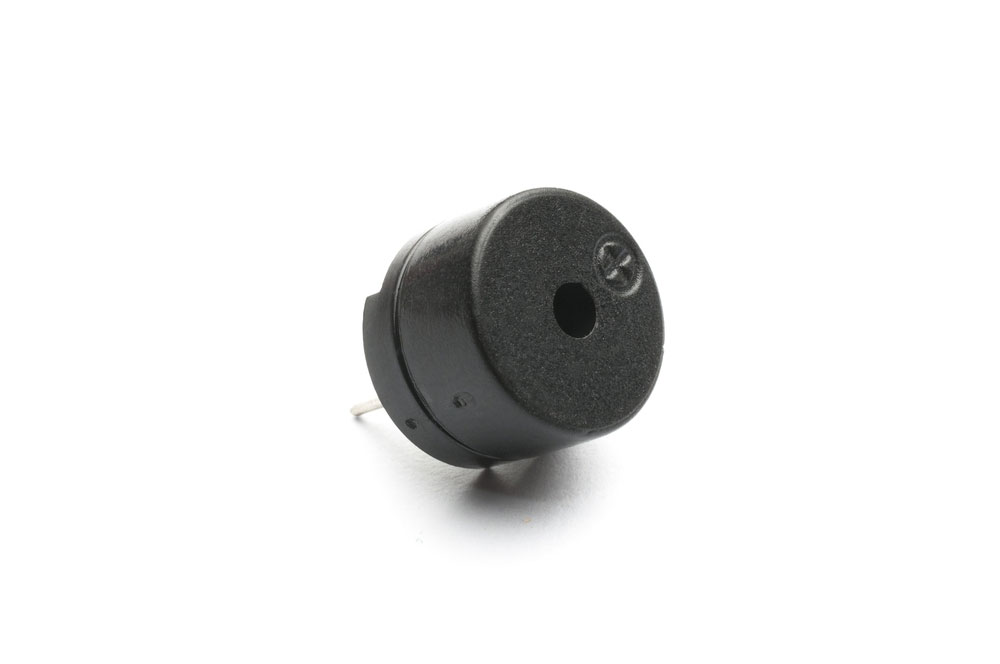

A piezo buzzer
Magnetic Buzzer
This buzzer consists of a magnet encapsulating a coil that wounds around a yoke. Above these components is a vibrating disk. Current passing through the coil pushes the disk forward, generating a sound pulse.
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Characteristics
Piezo and magnetic buzzers have the following characteristics.
Piezo Buzzer
- Wide operating voltage (3-250V)
- Low current consumption of less than 30mA
- High sound pressure level (85-120dB)
- Large footprint (7-50 mm)
- Highly rated resonant frequency (1-6 kHz)
Arduino piezo buzzer module component
Magnetic Buzzer
- Narrow operating voltage (1-16V)
- High current draw (30-100mA)
- Small footprint (4-25 mm)
- Low sound pressure level (70-95 dB)
- Lowly rated resonant frequency (1-3 kHz)
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Structure
These two devices have the following structures.
Piezo Buzzer
At the center of the piezo buzzer is a piezoelectric element. This section consists of a metal plate, and piezoelectric ceramic joined with adhesive. The ceramic plate has an electrode on each side for electrical signal conduction. After exposure to mechanical strain, piezoelectric materials exhibit piezoelectric and reverse piezoelectric effects. These effects cause the development of an electric field and vice versa.
Magnetic Buzzer
A magnetic buzzer comes either in an indicator or transducer configuration, just like the piezo buzzer. Indicators feature a transistor that functions as the driving circuit, creating a tone when connected to a DC input voltage. However, the transducer type does not have a transistor. Instead, it relies on a square wave signal to function properly.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzer: Working Principle
Piezo Buzzer
When AC voltage gets applied to the piezo element, it extends and shrinks diametrically because the voltage polarity alternates. This continuous expansion and shrinking cause the ceramic plate to vibrate rapidly, generating sound waves.
Magnetic Buzzer
Current flows through the solenoid in magnetic buzzers, creating an electromagnetic coil that attracts the vibrating disk. But since the current oscillates, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field. The disk vibration frequency is equal to the oscillating frequency, producing sound waves.
Variants of Buzzers
Apart from magnetic and piezo buzzers, the following are the three other buzzer variants.
Electromagnetic Buzzers
An electromagnetic buzzer contains a magnet, solenoid coil, vibration diaphragm, oscillator, and housing. Therefore, it functions as a magnetic buzzer because it generates sound waves via magnetism at 2 kHz.
Mechanical Buzzers
Mechanical buzzers are like subsets of electromagnetic buzzers because they have similar components. However, the vibrating parts sit on the outer casing, not in the internal structure of the buzzer.
Electromechanical Buzzers
Electromechanical buzzers consist of a bare metal disc and an electromagnet. They also function like a magnetic or electromagnetic buzzer by producing sound waves via magnetism and disc movement.
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Transducers and Indicators
Buzzers come in either a transducer or indicator configuration. Indicators have a built-in driving circuit that creates a plug-n-play buzzer. The advantage is that you won't have to worry about building a complex driving circuit for the unit. However, the downside is that such buzzers operate on a fixed frequency. Therefore, their design reduces flexibility and application areas because they can't achieve alternate frequencies for different uses.
On the other hand, transducers don't have a built-in driving circuit. Therefore, you have to build an external one to run the device. However, the lack of a driver is advantageous because it gives you more flexibility to achieve alternate frequencies. This flexibility makes the device ideal for multiple applications. Even though the external driving circuit can be complex, you can customize it for different uses.
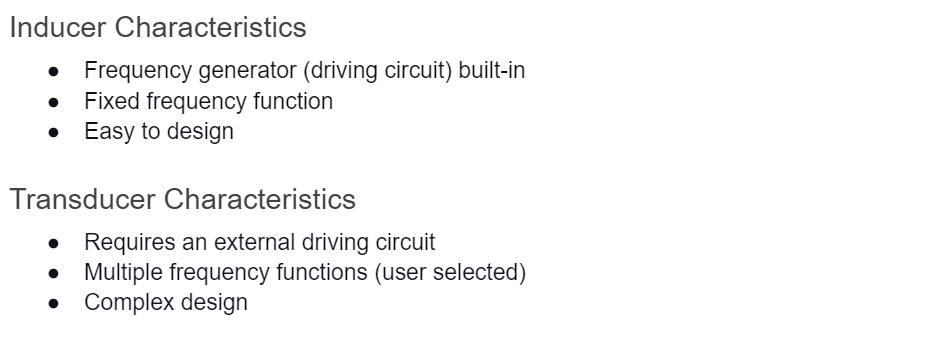
Another difference is in their tone generation. To generate a steady tone using a transducer, supply it with a continuous fixed frequency. However, indicators should get a constant DC voltage supply to produce such a tone.
On the other hand, producing a slow or fast sound wave using a transducer requires fixed frequency square wave pulses. However, to achieve the same using an indicator, apply PWM to switch it on and off.
Key Specifications of Buzzers
All five buzzer types have the following specifications.
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Frequency Response
A buzzer produces different sound pressure levels (loudness) for varying frequencies. Therefore, frequency response shows how efficiently the buzzer creates sound at specific frequencies.
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
Expressed in decibel Pascals, the SPL is an atmospheric pressure deviation created by sound waves. It is usually proportional to the input signal. Additionally, it decays by about 6dB as you double the distance away from the buzzer. The specification comes in handy when comparing two audio outputs to check which one is louder.
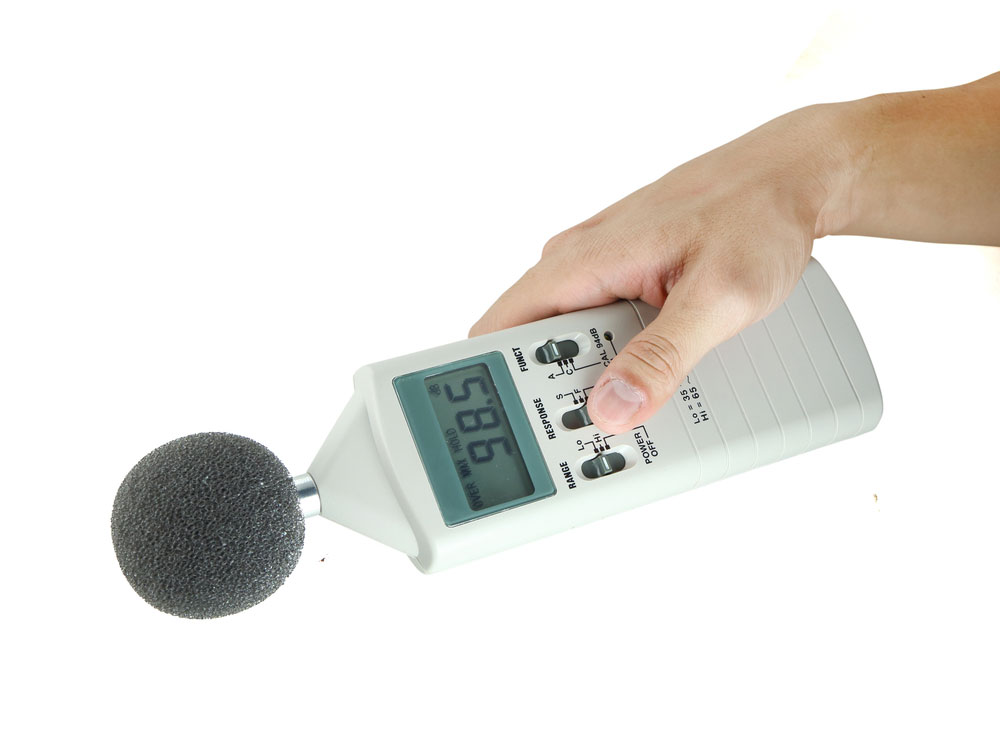

Sound level meter
Resonant Frequency
Measured in Hertz, resonant frequency is the buzzer vibrating frequency. Therefore, it can show the frequency at which it will be loudest.
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Operating Voltage
Piezoelectric buzzers are usually voltage-driven devices, and they have a wider operating voltage of 3-250V. On the other hand, magnetic buzzers are current-driven devices. Thus, they have a higher current draw and a narrower voltage range of 1-16V.
Impedance
Lastly, impedance is the ratio of the applied voltage to current, and it varies with frequency.
Piezo vs. Magnetic Buzzers: Applications


Home security alarm
- Electrical fire alarm
Summary
In conclusion, piezo and magnetic buzzers are the most common buzzer types, and it is vital to learn about their characteristics, structures, and working principles. This knowledge will make it easy to pick the right one for your project. After going through the article above, you should have a clearer understanding of the two. If you have any questions, contact us for more details.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!