PCB Types List
Below is a comprehensive list of PCB types, mentioning the most common kinds of Printed Circuit Boards, including their descriptions, features, and applications.
| PCB Type | Description | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided PCBs | PCBs with copper traces on only one side of the substrate. | - One conductive copper layer on the substrate - Simplest and most cost-effective type - Components and traces on one side only - Lowest production cost among all PCB types |
- Calculators - Electronic toys - Timing circuits - LED lighting systems |
| Double-Sided PCBs | PCBs with copper traces on both sides of the substrate. | - Two conductive layers (top and bottom) - Components can be mounted on both sides - Connected through plated holes (vias) - Allows for more complex circuits |
- Cell phones - Amplifiers - HVAC systems - Industrial controls |
| Multilayer PCBs | PCBs with three or more conductive layers, separated by insulating material. | - Minimum of three conductive layers - Current capability up to 40 layers - Common configurations: 4, 6, or 8 layers - High circuit density - Reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) |
- Computers - Medical equipment - GPS technology - Satellite systems |
| Rigid PCBs | PCBs made from solid substrate materials that prevent the board from bending. | - Made from solid substrate material (typically FR-4) - Durable and stable - Provides excellent mechanical stability - Cost-effective for standard applications |
- Motherboards - Memory modules - Telecommunication devices |
| Flexible PCBs | PCBs made of flexible substrate materials like polyimide. | - Can be bent, folded, or shaped - Excellent for space-constrained applications - Reduces weight compared to rigid boards - Made from flexible materials like polyimide |
- Wearable devices - Flexible connectors - Medical equipment |
| Rigid-Flex PCBs | Combines rigid and flexible PCB technologies in a single board. | - Combines rigid and flexible board materials - Allows for three-dimensional configurations - Reduces the need for connectors and cables - Improves reliability |
- Aerospace and military equipment - Consumer electronics - Smartphones |
| High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs | PCBs with a higher wiring density per unit area compared to traditional PCBs. | - Higher circuitry density per unit area - Features laser-drilled microvias, blind and buried vias - Uses microvias and finer lines/spaces - Allows for miniaturization - Improved electrical performance - Operates above 1 GHz frequency |
- Smartphones - Tablets - Wearable technology - Complex routing applications |
| High-Frequency PCBs | Designed to handle signals in the gigahertz (GHz) range. | - Specialized materials for RF applications - Uses materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) - Low dielectric constant and loss tangent - Controlled impedance - Low signal loss - Superior moisture resistance |
- RF communication systems - Microwave antennas - Telecommunications equipment - High-speed digital applications |
| Aluminum PCBs | PCBs with an aluminum metal substrate for better heat dissipation. | - Metal core for superior heat dissipation - Excellent thermal conductivity - Reduces thermal stress on components - High mechanical strength - Better thermal management - More expensive than standard FR-4 boards |
- LED lighting - Power converters - Automotive electronics |
| Metal Core PCBs | PCBs that use a metal core (usually aluminum or copper) to improve thermal management. | - Contains a metal base layer (usually aluminum) - Excellent thermal conductivity - Superior heat dissipation properties - Reduces thermal expansion - Increases mechanical strength |
- High-power applications - Power equipment - Automotive lighting |
| Embedded Component PCBs | Components are embedded within the PCB layers. | - Reduces overall board size - Provides better protection for components - Improved EMI shielding capabilities |
- Miniaturized devices - High-reliability applications - Medical implants |
| Sequential Lamination PCBs | Built up layer by layer in sequence through multiple lamination cycles. | - Allows for more complex multilayer designs - Better control of impedance - Supports high-density interconnects (HDI) |
- Advanced electronics - Aerospace systems - Military equipment |
| Mixed Technology PCBs | Combines different PCB technologies within a single board. | - Includes both through-hole and surface mount components - Offers design flexibility - Can integrate rigid, flex, and rigid-flex sections |
- Complex applications requiring diverse components - Industrial machinery - Communication systems |
| Thick Copper PCBs | PCBs with copper thickness greater than 3 ounces (oz). | - Superior current-carrying capacity - Better heat distribution - Enhanced mechanical strength at connector sites |
- High-power applications - Power supply systems - Solar power converters |
| Heavy Copper PCBs | PCBs with copper thickness between 4 oz to 20 oz. | - Excellent current handling capabilities - Superior thermal management - Supports high-density and high-power circuits |
- Power distribution applications - Electric vehicle charging stations - Industrial load testers |
| Backplane PCBs | Used to connect several PCBs together to form a complete system. | - High-speed signal integrity - Complex routing capabilities - Supports multiple connectors and slots |
- Servers and mainframes - Networking equipment - Data centers |
| Opto-Electronic PCBs | Integrates optical and electronic components on the same board. | - Uses special materials for optical transmission - Higher data transmission rates - Reduces signal loss |
- Fiber optic communications - High-speed data links - Optical sensors |
| Hybrid PCBs | Combines different material types and technologies in one PCB. | - Can mix rigid, flex, and other materials - Customized for specific applications - Offers unique design solutions |
- Specialized industrial equipment - Medical devices - Advanced consumer electronics |
| Microvia PCBs | Utilize very small vias (holes) to connect layers in multilayer PCBs. | - Enables higher component density - Enhances signal integrity - Reduces signal delays |
- High-speed circuits - Compact electronic devices - HDI applications |
| Ceramic PCBs | Made using ceramic substrates like alumina or aluminum nitride. | - Superior thermal conductivity - Excellent dimensional stability - High-temperature resistance - High-frequency performance |
- High-temperature environments - RF applications - Aerospace and military systems - Extreme environment applications |
| High-Tg PCBs | PCBs with a high glass transition temperature (Tg), indicating higher thermal resistance. | - Better performance at elevated temperatures - Improved mechanical stability - Enhanced chemical resistance |
- Automotive electronics - Industrial controls - Power converters |
| RF PCBs | Designed specifically for radio frequency applications. | - Specialized materials to minimize signal loss - Precise impedance control - Low dielectric constant and loss tangent |
- Wireless communication devices - Radar systems - Satellite communication |
| High-Speed PCBs | Designed for high-speed signal transmission with minimal loss. | - Controlled impedance traces - Low dielectric constant materials - Careful layout to minimize crosstalk |
- Telecommunications - High-speed data processing - Computing equipment |
| Halogen-Free PCBs | PCBs manufactured without the use of halogenated flame retardants. | - Environmentally friendly - Compliant with RoHS standards - Reduced toxic emissions when heated - Growing in popularity due to environmental regulations |
- Consumer electronics - Eco-friendly products - Devices where environmental impact is a concern |
| PTFE PCBs | PCBs made using PTFE materials for high-frequency applications. | - Low dielectric constant - Excellent for high-frequency applications - Superior moisture resistance - Stable electrical properties over a wide frequency range |
- RF and microwave circuits - Satellite communication - High-speed communication devices |
| Polyimide PCBs | PCBs made using polyimide materials known for high-temperature resistance. | - High-temperature resistance (up to 260°C) - Excellent dimensional stability - Good chemical resistance |
- Flexible circuits - Aerospace and military electronics - High-temperature environments |
| High-Temperature PCBs | Designed to operate reliably at high temperatures. | - Made from materials like polyimide or ceramic - Enhanced thermal stability - Resistant to thermal degradation |
- Oil and gas industry - Aerospace applications - Industrial machinery |
| Antenna PCBs | Specialized PCBs that function as antennas for wireless communication. | - Precise patterning for specific frequencies - Uses low-loss materials - Compact and integrated design |
- Mobile devices - GPS systems - Wireless networking equipment |
| Photoimageable PCBs | Use photoimageable solder masks for fine-line circuitry. | - High-resolution patterning - Ideal for fine-pitch components - Improved aesthetics and functionality |
- HDI PCBs - Microelectronics - Precision instrumentation |
| LED PCBs | Specifically designed for mounting Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). | - Excellent heat dissipation - Often use metal cores like aluminum - Optimized for thermal performance |
- LED lighting fixtures - Automotive lighting - Display backlighting |
| Transparent PCBs | Made from transparent substrate materials. | - Aesthetic appeal for certain applications - Allows light transmission through the PCB - Limited to low-temperature applications |
- Display technologies - Innovative consumer products - Decorative electronics |
| Custom PCBs | PCBs designed and manufactured to meet specific customer requirements. | - Tailored materials, layer counts, and designs - Meets unique performance needs - Can combine multiple PCB technologies |
- Specialized industrial equipment - Bespoke electronics - Prototyping and R&D projects |
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
PCB Types by Substrate Material
| PCB Material Types | Description | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Standard glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. | - Most common PCB material - Good electrical insulation properties - Cost-effective solution |
- Standard PCBs - Consumer electronics |
| Polyimide | High-performance polymer material. | - High-temperature resistance (up to 260°C) - Excellent dimensional stability - Good chemical resistance |
- Flexible circuits - High-temperature applications |
| PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | High-frequency substrate material. | - Low dielectric constant - Superior moisture resistance - Excellent for high-frequency applications |
- RF and microwave circuits - High-speed communication devices |
| Aluminum | Metal substrate used for thermal management. | - Excellent thermal conductivity - Superior heat dissipation |
- Metal Core PCBs - LED lighting |
| Ceramic | Substrate material with high thermal conductivity. | - Superior thermal conductivity - High-temperature resistance - Excellent dimensional stability |
- High-temperature PCBs - Extreme environment applications |
| PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) | High-performance engineering thermoplastic. | - Excellent mechanical and chemical resistance - High-temperature stability |
- Specialized applications - High-temperature environments |
Copper PCB Types & Thickness
| Copper Thickness | Description | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (1 oz/ft²) | Approximately 35 micrometers thickness. | - Standard copper thickness for general-purpose PCBs | - General electronic devices - Consumer electronics |
| High Power (2-3 oz/ft²) | Increased thickness for higher current capacity. | - Better current carrying capacity - Improved heat dissipation |
- Power supplies - High-power applications |
| Thick Copper (>3 oz/ft²) | Copper thickness greater than 3 oz. | - Superior current-carrying capacity - Enhanced mechanical strength |
- High-power applications - Solar power converters |
| Heavy Copper (4-20 oz/ft²) | Copper thickness between 4 oz to 20 oz. | - Excellent current handling - Superior thermal management |
- Power distribution - Industrial load testers |
(Printed circuit board and component diagram)

(High computer technology on abstract circuit board)
(An insight of a Breadboard)
(Circuit board type-single panel picture)
(Double-sided welded board on white background)
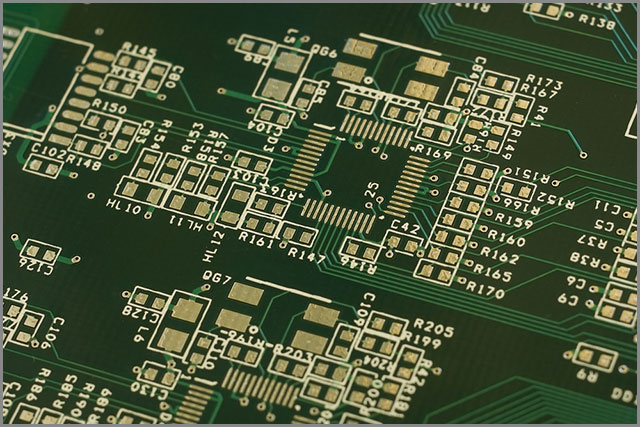
(PCB Type-Picture of Multilayer Circuit Board)
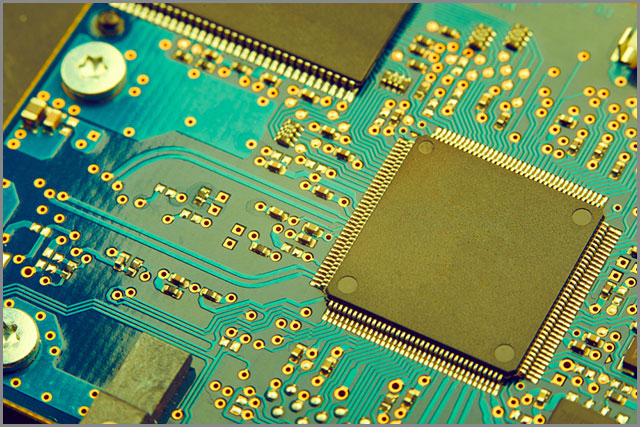
(A close-up on the use of a PCB In a motherboard)
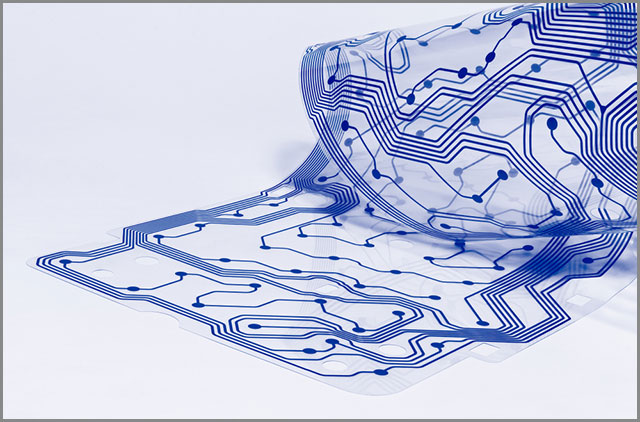
(Circuit board type-electronic flexible circuit board)

(High-frequency copper wire on the circuit board)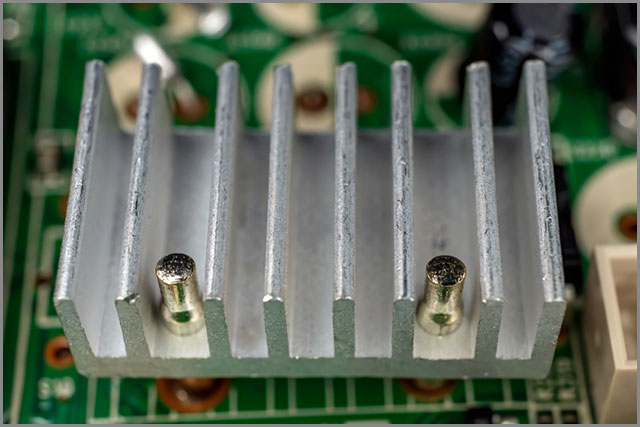
(An aluminum radiator prototype)
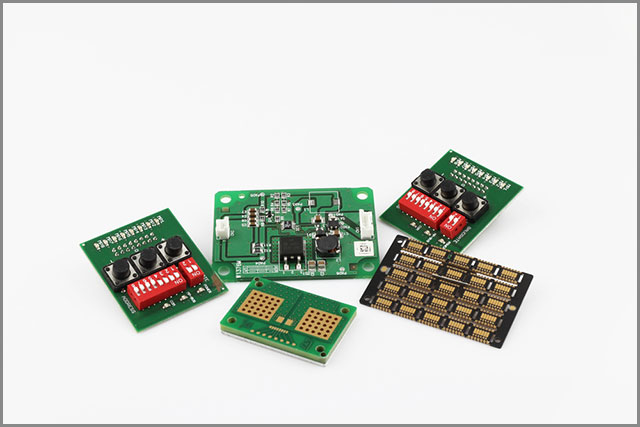

(Display a plurality of types of circuit boards)
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!






