MOSFETs can turn on and off like switches. But they can switch faster than standard bipolar junction transistors. Additionally, you can drive them to turn on slower or quicker or pass low or high currents. The IRLB8721 is one example of a MOSFET. More specifically, it is an N-channel, 30V logic level power MOSFET. The characteristics above give it multiple switching applications, and we have covered the device in detail below. Take a look!
Contents
What is IRLB8721?
The IRLB8721 is a power MOSFET optimized for high current and low RDS(on) capabilities. A MOSFET is one of the insulated gate field-effect transistors fabricated by the semiconductor's controlled oxidation.
Since the IRLB8721 is a power enhancement mode MOSFET, the enhancement part means the device's gate voltage is zero when it is off.
As for the power part, power MOSFETs are usually used as switches to control high-power LEDs or motors. They can handle up to 30V (at 62A) but are 5V logic compatible.
Lastly, N-channel MOSFETs are the most common types and are easier to work with in different applications.
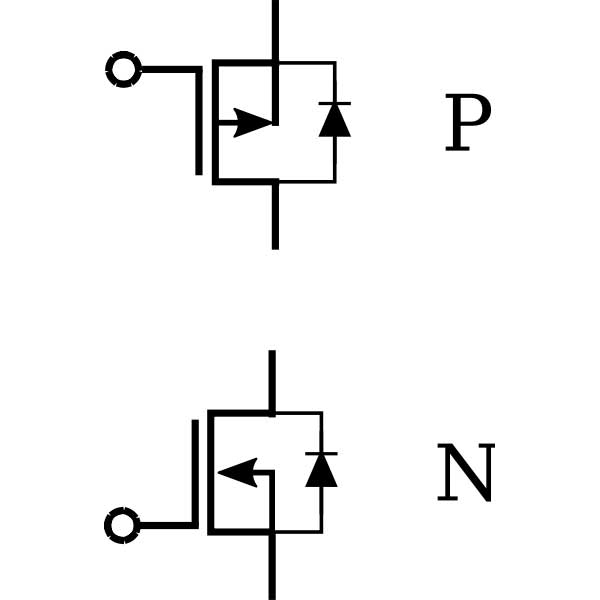
A P-channel vs. N-channel power MOSFET
Source: Free SVG
IRLB8721 Pinout
This N-channel MOSFET only has the following three pins.
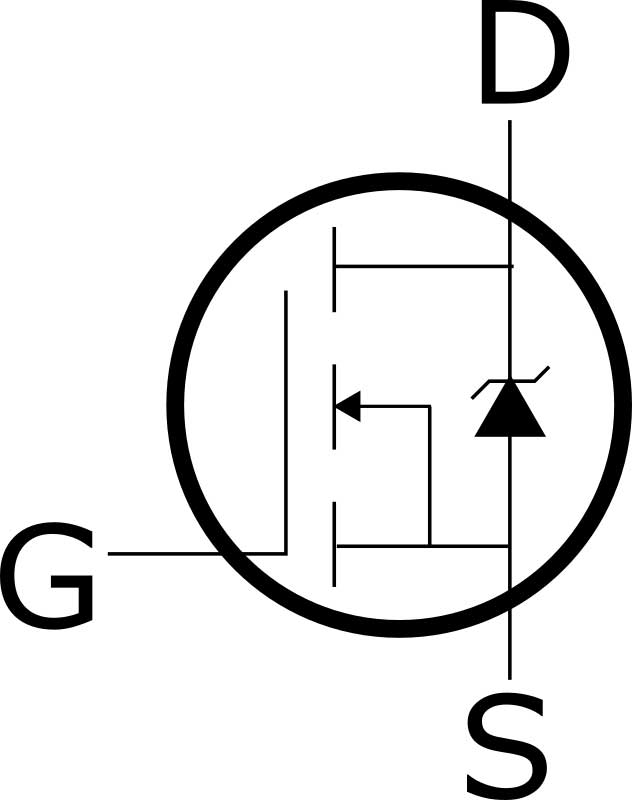
Pins in an N-channel MOSFET
Source: Open Clipart

IRLB8721 Features
- Through-hole power package (industry standard)
- High current rating
- Available in a broad portfolio
- Softer diode body than the earlier silicon generation
- JEDEC standard product qualification
- Optimized with silicon for switching applications below 100kHz
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
IRLB8721 Benefits
- Industry-standard qualification level
- High power density
- High current carrying capability
- Provides the flexibility to pick the most optimal device for specific applications
- Performs well in low-frequency applications
- Standard pin arrangement for drop-in replacement
- Lead-free
- Ultra-low RDS(on) at 4.5 VGS
- Low gate impedance
- Wholly characterized avalanche voltage and current
Potential Applications
- Areas requiring battery power
- DC motors

A DC motor
- System load switches
- UPS/Inverter applications
- Isolated DC-DC converters (high frequency) with synchronous rectification for industrial and telecom use
A DC-DC converter
Source: Wikimedia Commons
- Synchronous buck converters (high frequency) for computer processors
A voltage/buck converter (5V to 3.3V) for 80486 dx4 processors
Source: Wikimedia Commons
N-Channel MOSFET Theory of Operation
Even though MOSFET spec sheets look pretty complicated, you only need to look at the following parameters.
An N-channel power MOSFET
Source: Wikimedia Commons
This parameter refers to the max voltage the device can switch. For instance, when switching 5V, you should get a MOSFET with a VDS rating of over 5V. Ensure to give it a considerable allowance to improve the safety margin.
The continuous drain current is the max current the MOSFET can handle. Usually, this parameter will vary depending on multiple conditions, such as at room temperature (25°C) and 100°C. But achieving the max current through the MOSFET assumes it has the proper heat sink, and you are driving it full-on to the saturated region. A higher ID rating than the current you want to pass through is always better because it makes it easier to manage the thermals.
The gate voltage is the voltage differential between the gate and source. It shows how hard you are driving the MOSFET.
This parameter is the voltage at which the device begins conducting. Any voltage below this value will drive the MOSFET to the cut-off region or off state. This parameter should be lower than the logic high voltage level to be logic-compatible.

For instance, if specified at 10V only, the MOSFET is not logic compatible and needs about 10V or close to that to drive it into saturation. Technically, this rating implies you need a transistor, MOSFET driver, or any other device with close to 10V to turn on the MOSFET.
A power MOSFET that closely resembles the IRLB8721
Source: Wikimedia Commons
If the device has two voltage ratings, the highest of the two (usually 10V) will be the level at which the device attains saturation and has the lowest resistance. On the other hand, the lowest rating (typically 4.5V) shows the MOSFET's resistance if you drive it directly using 5V logic.
Summary
In conclusion, IRLB8721 MOSFETs are reliable switching devices that you can use in various applications for your project. If you need further clarification or want to make a comment/suggestion, leave a message in the contact section, and we'll get back to you asap.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!