Circuit boards have multiple connection points, and while you can solder different components on board, this method is not practical when testing or prototyping. The best solution for such applications is to use circuit board headers.
Circuit board headers simplify connections to the board because they form a wire-to-breadboard link type, which you can plug and unplug multiple times. You only have to solder one side of the header to the board, then use individual wires/ribbon cables to link components to the header connector.
We will shed some light on these headers below, including their types, terminology, board applications, and more. Let's take a look!
Contents
- What are PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Headers?
- Why Use PCB Headers?
- PCB Header Types
- Machine Pin Headers
- Angled Connector Headers
- Single and Double Row Pin Headers
- Important Connector Terminology
- Polarity
- Gender
- Pitch
- Contact
- Mount
- Mating Cycle
- Strain Relief
- Printed Circuit Board Header Classification
- Applications of Printed Circuit Board Headers
- How Box Headers Differ From Female Headers
- Summary
What are PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Headers?
PCB headers are electrical connectors that enable you to create connections on a PCB board via a single connection block. Typically headers have two sides, one for surface mount soldering on the board and the other for making the electrical connections.
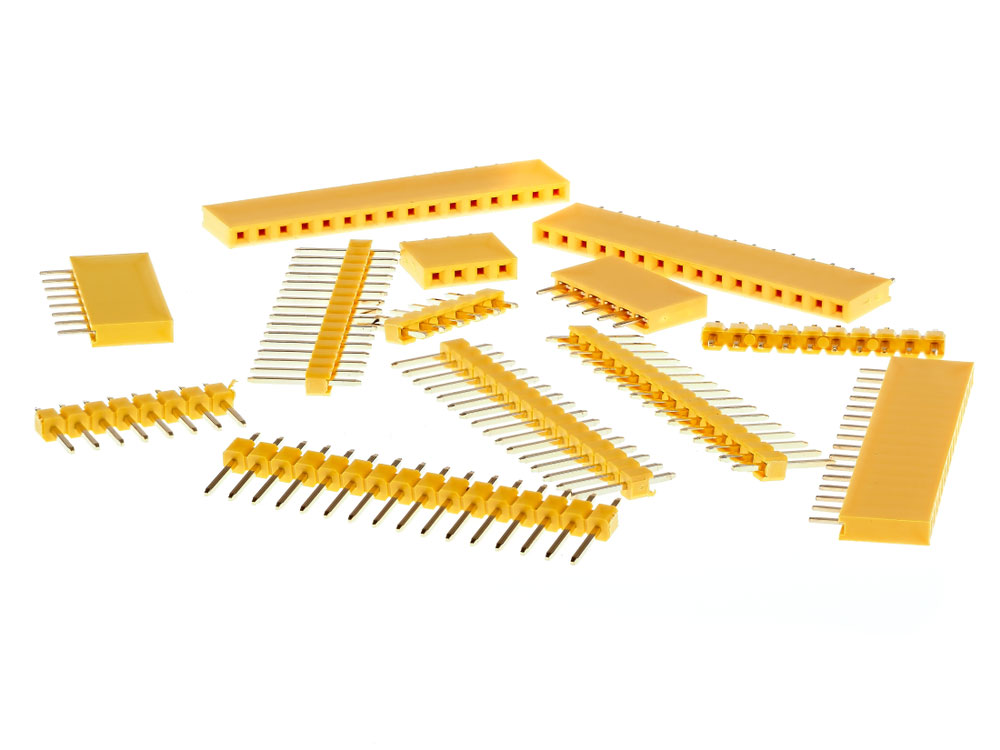
Male and female single row pin header connectors
Also, they can either be shrouded or non-shrouded pin header types. A shrouded pin header connector has a protector surrounding the pins to allow locking, prevent pin bending, and make the header more secure.
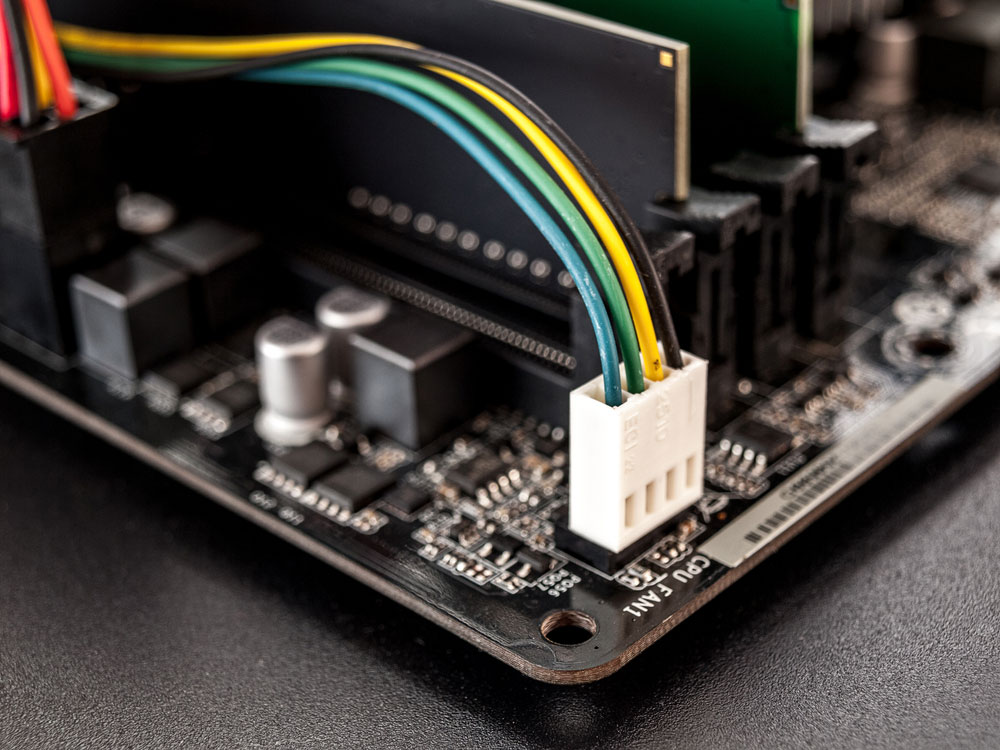
A 4-pin box/shrouded PCB header connector with individual wires
Why Use PCB Headers?
Consider using PCB headers because they have the following advantages.
- Easy to use
- Enable multiple electrical connections to a PCB using a single block or cable
- Each pin is multipurpose (can carry power or data)
- Simple to understand because they have one primary purpose (allowing wire-to-board connections). Therefore, they are ideal for learners working with single-board computers like Raspberry Pi and Arduino.
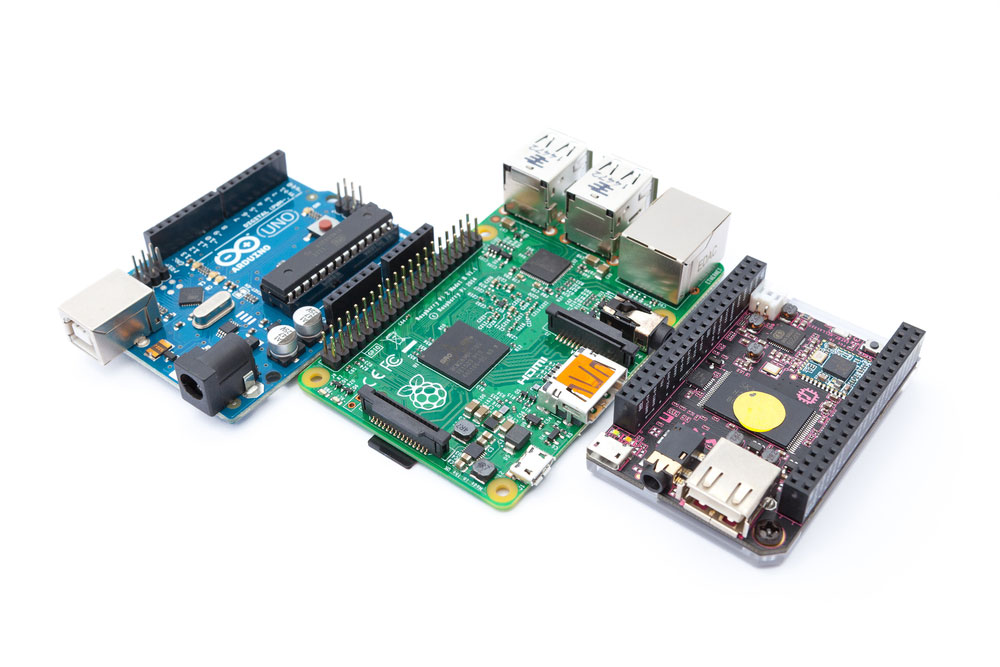

Three single-board computers (Arduino UNO, Raspberry Pi, and C.H.I.P)
PCB Header Types
There are three types of PCB headers. They include:
Machine Pin Headers
Machine pin connectors feature a circular cross-section to enable them to fit in round PCB holes. Since they fit into the round slots, they provide better electrical connections, are more durable, and have longer lifespans.
Angled Connector Headers
Angled headers come in several angle configurations. But the most common angles are 90° and 180°. They are perfect when you need more room vertically or horizontally above the board or when you want to minimize cable strain.
Single and Double Row Pin Headers
Single and double row pin headers are the most typically used PCB header types. As the name suggests, the former has one row of pins while the latter has two rows of pins. Both board connectors come in matching male and female versions and consist of a folded metal sheet with a square cross-section.
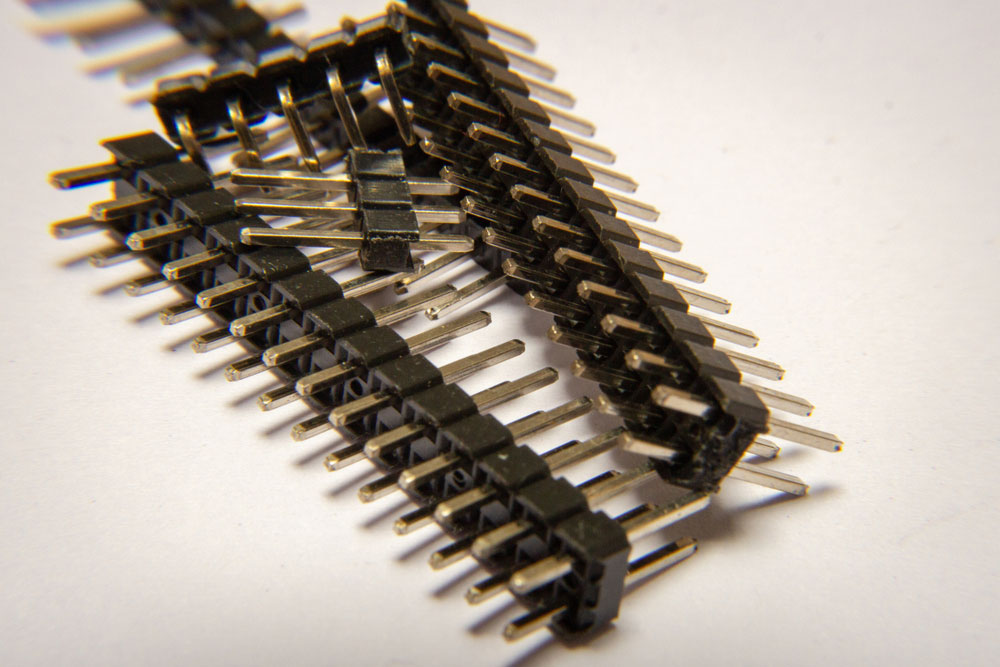
Double row male pin headers
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Important Connector Terminology
Like most other electronics, board connectors have some technical terminologies that you should understand. The most vital ones include the following.
Polarity
Most connectors allow electrical connections in one orientation. These keyed or polarized pin header connections usually have mechanisms to prevent wrong orientation/incorrect connections.
Gender
Board connectors can be male or female, and this gender refers to whether the header plugs into the board or gets plugged into, respectively.
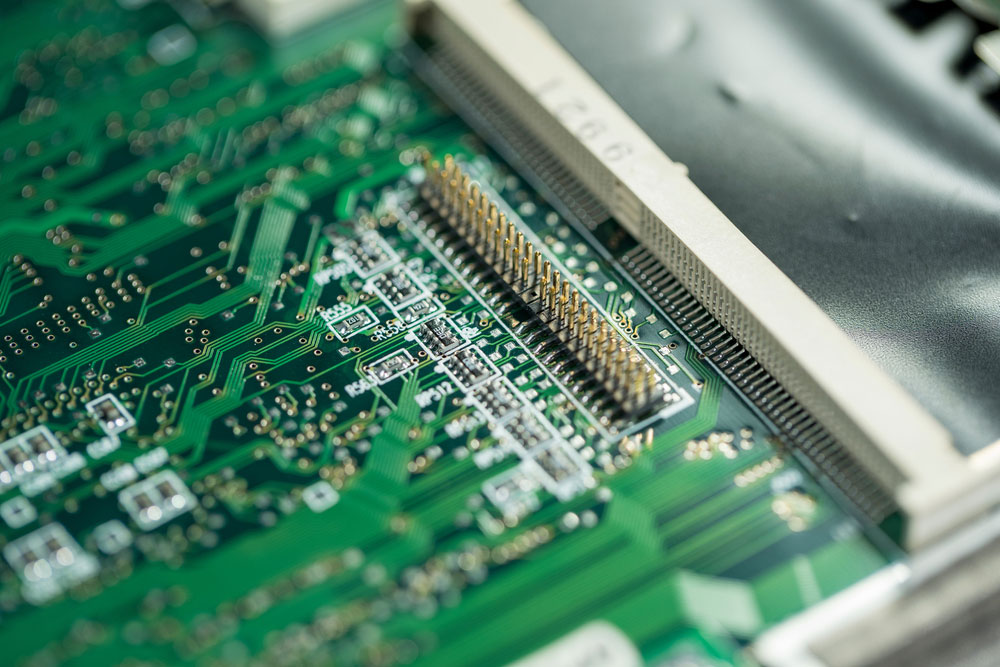
A computer circuit board with a male pin header attached
Pitch
These board connectors usually contain several contacts arranged in a repetitive pattern. Pitch defines the distance from a contact's center to the center of the adjacent contact. This factor is vital because it helps determine perfectly mating connectors. These headers might look the same, but their pitch can differ.
Contact
This term refers to the business-end part of the connector. Most are metallic to maximize sturdiness and establish an electrical connection. However, this part can get soiled or oxidized. Also, the springy characteristic that helps secure the contacts can reduce with time.
Mount
Mount refers to several things. First is the connector mounting on the panel, which can be board-mount, free-hanging, or panel-mount. Also, there's the mechanical attachment manner to the board (through-hole or surface mount) and the connector angle relative to its attachment (straight and right-angle headers).
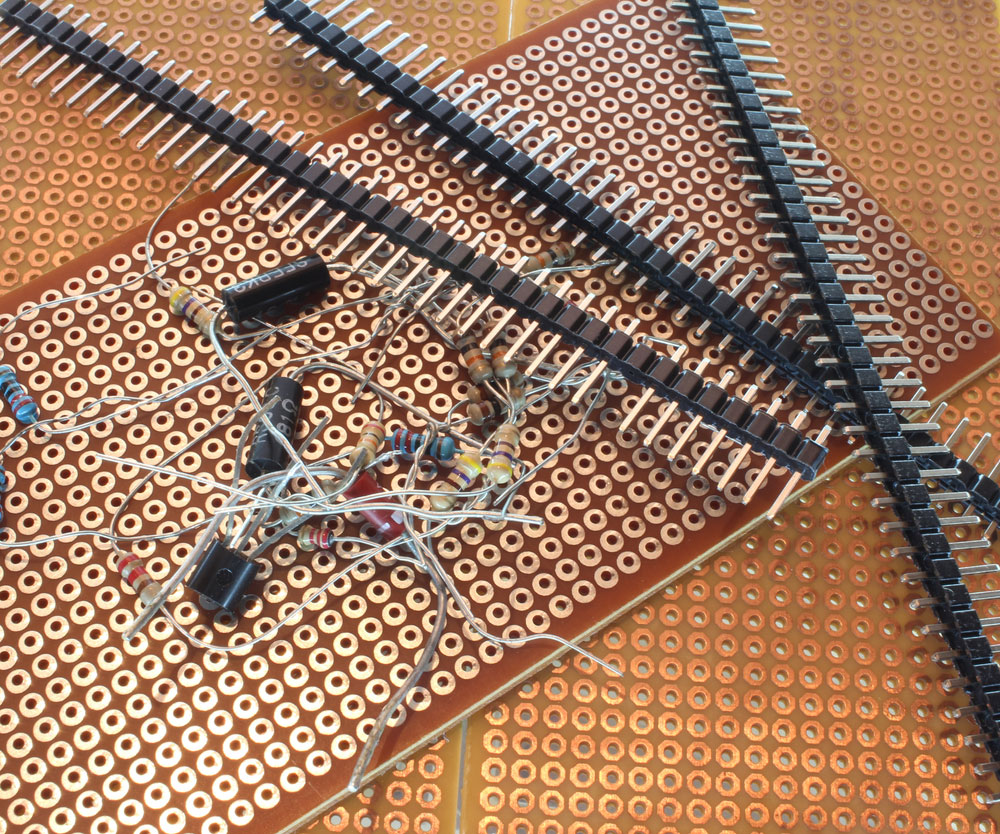
A prototyping board with pin headers
Mating Cycle
All board connectors have a specific lifespan because the regular connection/disconnection wears them out. For comparison purposes, a board-to-board connector for consumer electronics can have a mating cycle of 10-100, while a USB connector can have thousands. The higher the mating cycle, the longer the lifespan.
Strain Relief
This term refers to the relief provided to a cable or board-mounted connector and its fragile electrical connection. Strain relief ensures a strong, steady, and reliable connection by deflecting any pressure from the electrical link to mechanical components.
Printed Circuit Board Header Classification
While there are several PCB header types, these fall into specific classifications that place them in the following broad categories.
- Screw terminal header
- Right-angled PCB header
- Multiple row PCB header
Applications of Printed Circuit Board Headers
- Xbee PCBs, LCD circuit boards, and a similar range of applications
- Evaluating printed circuit boards and other crucial consumer electronics
- Computer power supplies (especially those linking to the floppy drive)
- Ensuring proper functionality in motherboards
- Paired with jumper wires to form semi-permanent input devices
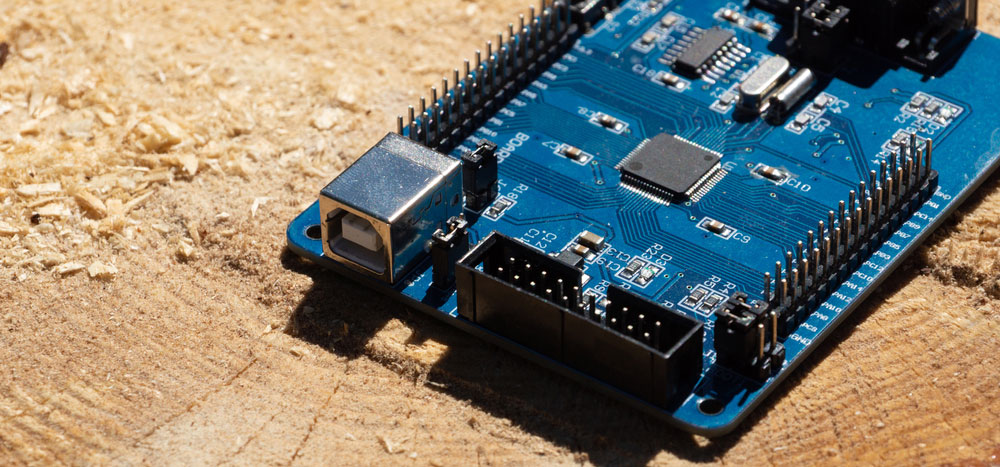
A single board computer with double row pin connectors on both sides
How Box Headers Differ From Female Headers
A box header is the same as a shrouded PCB mount header. It features an outer cover around the pins rising from the plastic base. However, this rectangular enclosure does not imply the connector is female, even though it appears to get plugged into like the female type.
The primary purpose of this enclosure is to keep the connector in place once plugged into the female slots. Therefore, the connector cannot be female. It goes around male pins.
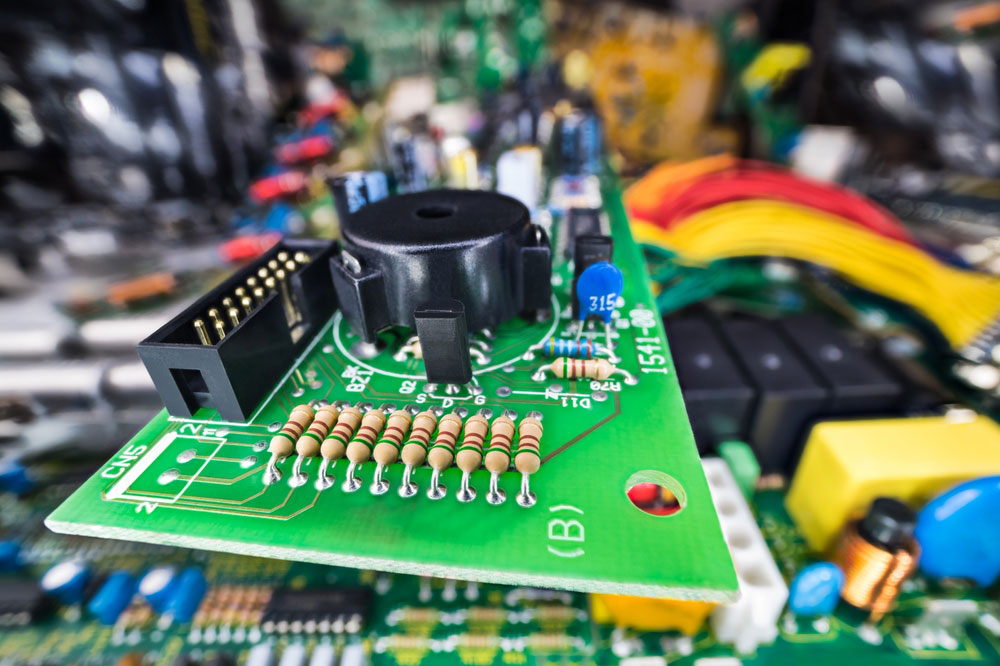

A box header with male pins mounted on a circuit board
Another function of the cover is preventing incorrect connections because it contains a notch for blocking reverse pin header connections. This feature is similar to the anti-reversal technique in a polarized board connector system.
A female header connector behind RCA connectors
The anti-reversal mechanism usually involves one filled socket connector pin in the female version. Similarly, there is a clipped pin at the corresponding spot on the male socket connector. The two form a blanked connection that prevents incorrect insertion.
Summary
In conclusion, circuit board headers are simple but critical electrical connection blocks for prototyping, learning, and multiple other applications. However, they come in different types and have several terminologies you should learn to pick the right piece for your project. We hope this article has been insightful and if you have any questions or comments, leave a message, and we'll respond asap.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!