The heat shrink tubing technique covers or encases cables or wires to seal an environment. You can also refer to the heat shrink tubing as heat shrink sleeves.
The heat shrinking procedure is not as complicated as most people think. You have to get one, insert the wire, and heat the sleeve for insulation. Plus, there's a wide range of shrinks in the market.
Here we'll discuss why we use heat shrinks, factors to consider when heating them, and the available types.
Contents
- Why Should We Use Heat Shrink Tubing?
- Rust Protection
- How to select an appropriate heat shrink?
- Shrinkage Ratio
- Selecting the Internal Diameter
- The thickness of the Tube
- Shrink Tube's Length
- Standard Heat Shrink Tubing Materials and Required Temperature
- Polyolefin
- PVC
- Adhesive Lined Heat Shrinks
- PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing
- FEP Heat Shrink Tubing
- Elastomeric Heat Shrink Tubing
- PVDF Heat Shrink Tubing
- Silicone Heat Shrink Tubing
- Viton Heat Shrink Tubing
- FAQs
- Can You Use Electrical Tape Instead of Heat Shrink Tubing?
- How to Use Heat Shrink Tubing Without a Hot Air Gun
- Conclusion
Why Should We Use Heat Shrink Tubing?
Rust Protection

Rusty Wire
Source: Google Images Creative Commons Licenses
The heat shrink tubing has several benefits. These include:
- Adequate wire protection against low impacts, abrasion, and other hazards
- Thermal and electrical insulation
- Create a defensive mechanism against dust, acids, water, oil, and other contaminants
- Bundling cables in sophisticated networks to ensure they're well-organized
- Creating more strength to prevent strain on wires and cables
- Create a smooth texture and appealing appearance
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
How to select an appropriate heat shrink?
Shrinkage Ratio
It is the ratio between the inner diameter supplied and the recovered inner diameter. For example, a percentage of 4:1 means that the Tube can shrink to a quarter of its original size.
A shrink tube with a high shrinkable ratio can be very effective in objects such as connectors. It can enclose the connector's body and shrink to a smaller diameter, e.g., a wire.
Selecting the Internal Diameter
To get the correct internal diameter, you have to look at the minimum and maximum diameter of the object. We recommend an inner diameter between 20% and 30% allowance. It will provide enough space to ensure the shrink merges with the thing.
The two main things you should consider in this area include:
- Inner diameter-recovered: The minor diameter obtained after you heat the shrink
- Inner diameter-supplied: The nominal diameter before heating the shrink
The thickness of the Tube
The Tube may shrink and increase in thickness when you heat it. Hence, you should ensure that you select a heat shrink material that suits your working environment.
Shrink Tube's Length
The length of the shrink tube may reduce when you heat it. Therefore, you should ensure that it allows between 5% and 7% when you heat it.
Standard Heat Shrink Tubing Materials and Required Temperature
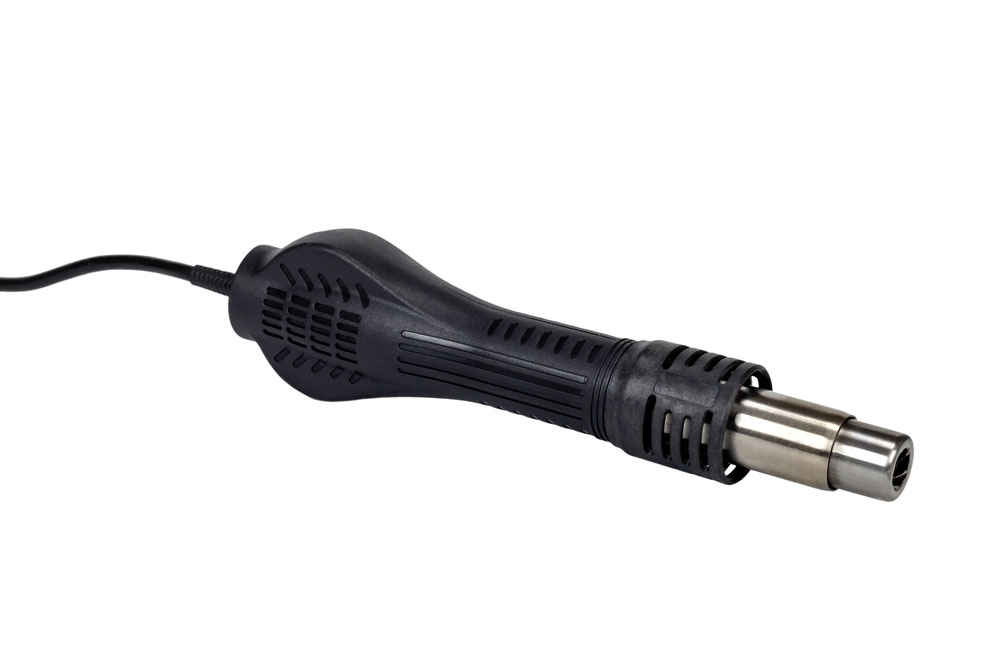

Hot Air Gun
Polyolefin
This material has several advantages, such as:
- Quick shrinking
- High flexibility
- Incredible durability
It shrinks at temperatures of 100°C but can withstand up to 135°C.
PVC
These shrinks consist of Polyvinyl chloride. They can withstand up to 105°C. This shrink is 10% to 50% less expensive than the Polyolefin shrink and is available in several colors. Besides, they display better abrasion resistance and strength.
Adhesive Lined Heat Shrinks
This heat shrink has two layers: The outer polyolefin layer and the Inner adhesive layer.
Once you heat it, the inner adhesive layer melts and flows, filling the void and creating an intact environmental seal.
PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing
This tubing is ideal if you want protection against high temperature (Up to 260°C) and chemical resistance. It comes in an expanded state and shrinks once you apply heat, forming an impenetrable shield.
FEP Heat Shrink Tubing
These shrink tubes consist of Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene, which is highly durable and can withstand high stretching. The Tube's shrinking temperature is around 180°C, but it can withstand consistent temperatures between 200°C and 205°C.
Elastomeric Heat Shrink Tubing
This heat shrink tube consists of Elastomers, a class of Polymers with elastoviscosity (elasticity & viscosity). The material can withstand temperatures above 150°C, and its shrink ratio is 2:1.
PVDF Heat Shrink Tubing
PVDF heat shrink tubings are famous for their high resistance to cold flow, abrasion, and impact. The PVDF is transparent, and its minimum shrink temperature is 175°C.
Silicone Heat Shrink Tubing
This shrink tube can withstand extreme heat conditions of up to 175°C. It is water-resistant, and its average shrinkage ratio is 4:1.
Viton Heat Shrink Tubing
Viton belongs to a class of fluoropolymers that are highly resistant to chemical erosion. Besides, it can withstand a maximum temperature of 200°C and has an average shrinkage ratio of 2:1.
FAQs
Can You Use Electrical Tape Instead of Heat Shrink Tubing?

Electrical tape
Yes, in some cases. However, the heat shrink tubing is more durable and safer than electrical tape. Hence, you'll have to do a regular inspection to ensure the electrical tape is in excellent condition.
How to Use Heat Shrink Tubing Without a Hot Air Gun

Blow dryer
If you don't have access to a gun for heat shrink, you can use a blow dryer instead. It operates in the same way. Hence, you'll have a smooth time using it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat shrink tubing is necessary if you want maximum protection for your wires and cables. However, you should ensure that you double-check its key features before you purchase one. Besides, there are several types of heat shrink tubings that you can consider.
That said, you can contact us on our page if you have any questions.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!