Electronics are part of our lives and integrate deeply into almost every aspect to the point that we cannot do without them. So using conductive paint to experiment with electronics or build flexible circuits can have several advantages. We will take a closer look into electric paints to see the types and show you how to make some for your project. Take a look!
Contents
What is Conductive Paint?
As the name suggests, conductive paint is a paint variety with conductive materials to give it conductive properties. These conductive particles include materials like graphite powder or metal particles mixed in a liquid medium.
Current moves through the paint from one nanoparticle to the other. So these conductive particles should have a high concentration to create a tight pack and provide bridges for transmitting the electrical charge. Although you can measure particle concentration, there's still some randomness involved when determining the effectiveness of conductive paint.
But the particles must be ultra-fine to maintain regular paint's characteristic binding and wetting properties.
Types of Conductive Paint
There are several conductive paint products in the market, but all fall into one of the following categories.
Carbon-Based Electric Paint
Graphite is an alternative to carbon because it is a crystalline form of carbon. So it is more typical than carbon-based electric paints. Also, it is one of the best alternatives to metal because the material is abundant on Earth, oxidation resistant, and stable in high temperatures.
The material gets ground to ultra-fine particles, then mixed with paint to make it conductive. And since it does not oxidize, you can dissolve the powder with water-based paint, which is less toxic and solvent-free. Once applied, the paint dries at room temperature and does not need curing.

Graphite powder
But this carbon-based paint is not waterproof. So you should apply a waterproof coating above it, such as acrylic varnish.
However, the biggest drawback of graphite-based conductive paint is its lower current transmission capacity than metal. Graphite material relies on charge localization for conductivity, unlike ion migration in metals. This phenomenon makes it slower when transmitting current, limiting its applications.
Metal-Based Electric Paint
Metallic paints are more typical due to their high conductivity. They support higher current transmission than graphite-based conductive paint, making them ideal for high-load applications.
They contain metal nanoparticles like silver or copper because the metals are soft (malleable) and highly conductive.

Silver metal granules in a glass flask. The nanoparticle powder must have smaller particles.
But metals have their drawbacks too. For instance, they are prone to oxidation, meaning a limited shelf-life. Also, they need a solvent-based medium to simulate the paint characteristics. This medium creates flammability and ventilation hazards. Metallic paints can be costly, as well, because they are difficult to source and experience price fluctuations.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Electric Paint
Electric paint is revolutionary but can't replace solid metal conductors. So here are its pros and cons.
Pros
- Flexible medium: Arguably its most significant advantage, flexibility makes it possible to integrate electric paint in mediums like fabric and paper.
- Flexible application: Flexibility extends to its application methods. You can apply the paint by brushing, painting, printing, or screen-printing. These application methods make this paint ideal for automated manufacturing processes.
- Ease of use: Everybody knows how to paint, but not everyone can make circuits using wires and breadboards. This ease of use makes electric paint ideal for learning/experimenting or quick repairs.

Electric paint, copper paint
Cons
- Low conductivity: These paints cannot be as conductive as their solid counterparts because transmission relies on contact with adjacent particles.
- Poor durability: The flexibility of conductive paint implies a lack of durability. So this paint is not ideal for rugged applications.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
DIY Electric Paint: How To Make
Conductive paint is costlier than regular paint due to the cost of the graphite or metal particles. So if you want to save some cash, you can make some as a DIY project.
The process involves adding an electronically conductive pigment into a non-conductive resin binder. This binder holds the paint together and offers adhesion.
We will make the graphite-based type because graphite material is easier and cheaper to buy than metallic nanoparticles.
Pour the powder into a non-conductive liquid to suspend and spread it uniformly. You can use white glue or acrylic paint. The goal is to attain a thick consistency that can create thin, consistent coats.

White glue spilled on a piece of blue paper.
Glue is cheaper than acrylic paint and can make a binder up to 20X less costly than the ones available in stores. Plus, the quality of this glue is comparable to the commercial one. So you should only ensure the conductive material is of high quality.
Conductive Paint vs. Conductive Ink
Conductive paints and conductive inks refer to the same thing. But they have minor differences in their usage and applications.
Paint gets applied to the substrate or medium and sits above it. And its application methods usually include brushing or spraying. On the other hand, the ink gets printed onto the medium (fabric or paper) and penetrates through.
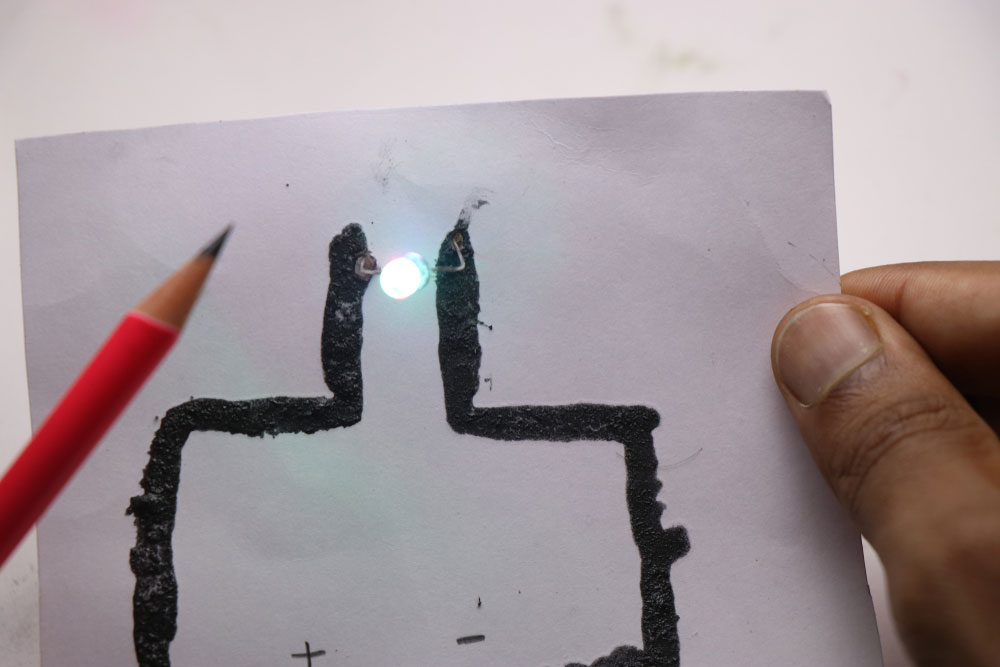

Conductive ink from a pencil’s graphite lighting an LED
So the primary difference between the two usually has to do with the substrate/medium and application method. Also, ink is more suitable for small-scale applications, while the paint is ideal for large projects.
Applications of Conductive Paint
- RFID tags (access cards and train tickets)
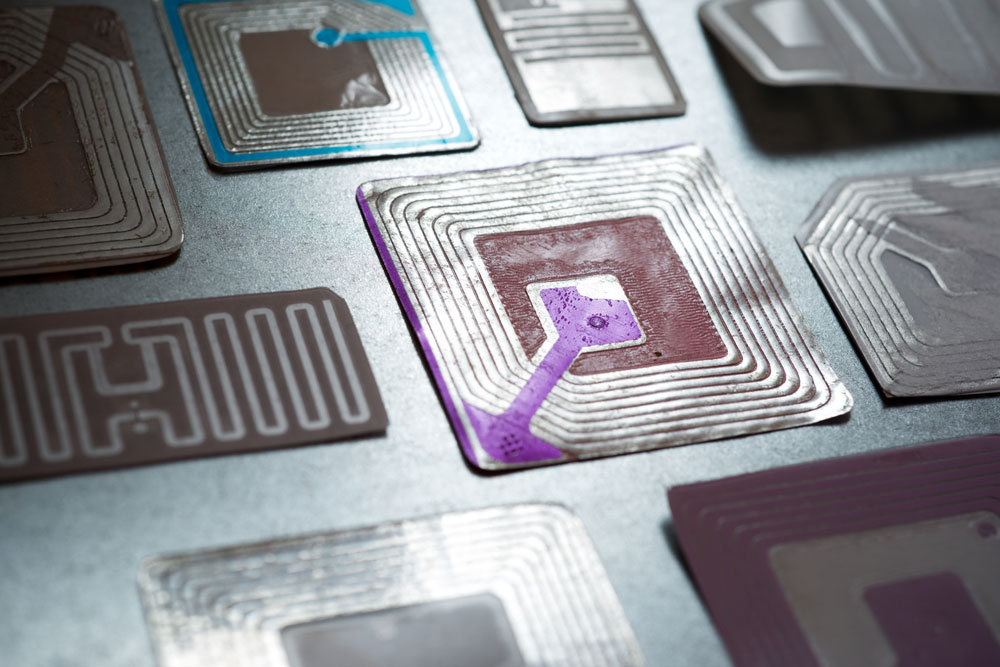

RFID tags on a table
- Cold soldering to create simple conductive bridges
- Education
- Wearable technology, especially fabrics
- Quick repairs
- EMI/RFI shielding
- ESD protection
- Electroplating plastics
- Galvanic corrosion resistance
- Grounding surfaces
Terms Associated With Electric Paint
While working with electric paint, you might encounter some of the following terms.
- Conductive Acrylic Paint: An easy-to-apply one-part coating that cures quickly and gives optimal shielding from RFI and EMI to plastic electronic enclosures.

Acrylic paints
- Conductive Epoxy Paint: Super adhesive 2-part coating that is highly durable and chemical resistant. It is ideal for use in harsh applications.
- ESD Safe Coatings: These durable coatings help prevent electrostatic discharge on the substrate.
- Board and Package-Level Shielding Coating: This coating is suitable for short-range, high-frequency EMI tasks. Heavy-duty versions that can resist wave soldering are available. These variants do not fray when cut.
- Water-Based Conductive Shielding Paint: This single-part coating is suitable for application on wood, such as on guitars and other musical instruments. Also, you can apply them on drywalls, walls, and other architectural parts.

An open can with water-based paint.
- Conductive Pens: As the name suggests, these pieces come in the form of a pen. They are ideal for trace repairs, touch-ups, and prototyping.
- Conductive Paint Thinners: Thinners make paints lighter. So conductive paint thinners make the liquid less viscous.
- Conductive Spray Paints: These are convenient aerosol packages of conductive acrylic paints.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, conductive paint cannot replace solid electric conductors, but its flexibility and ease of use make it suitable for some unique applications. And as you can see above, it is possible to create the paint as a DIY project. That's all for this article. Thanks for your time.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!