Printed circuit boards are all over. Think of the electronic products that you have come across. They all have a printed circuit board as the fundamental piece in their makeup. Unfortunately, a relatively high number of electronic scraps also imply that many PCBs go to waste. Still, the waste circuit boards can help assemble electrical components. Thus, it's essential to have a recycling process for these valuable materials. In that regard, our article will delve into the essence of recycling PCBs. Furthermore, it'll expound on the printed circuit board fabrication process, highlighting the importance of reusing materials to minimize waste.
Contents
- Why Recycle PCB?
- What Are the Challenges in Circuit Board Recycling?
- How to Recycle Circuit Boards?
- Thermal Recovering
- Chemical Recovering
- Physical Recovering
- Circuit Board Recycling Process
- Pyrometallurgy
- Hydrometallurgy
- Electrochemical Process
- What You Can Recycle from Printed Circuit Boards
- What Parts of the Circuit Board Are Worth Money?
- Can You Make Money From Recycling Circuit Boards?
- Can PCB Recycling Processes Harm the Environment?
- How to Make PCBs More Recyclable?
Why Recycle PCB?

Electronic Waste
People casually disposed of electronic waste and other hazardous materials in the past. However, the electronic industry has grown bigger, implying more destruction than ever. Thus, the recovery of materials is more important than ever.
We can use it as a raw material for other electronics rather than the waste circuit board finding its way in pits.
What Are the Challenges in Circuit Board Recycling?
The challenges of recycling printed circuit boards stem from the fact that these products contain different materials like fiberglass, plastic, and metal.
On top of that, assembled boards have multiple surface-mount and through-hole components that are part of the recycling process.
Therefore, you have to sort the boards before disassembling the components first.
While disassembling these parts, you have to manage the hazardous materials, especially if the welding filler material is Lead solder.

A heap of e-waste from discarded laptop PCBs and parts
The board also has precious and valuable metals like gold for the surface finishes, and you have to extract them carefully, as well, because they can fetch good returns.
Generally, separating these materials to maximize recycling and returns is the most challenging part of the process.
How to Recycle Circuit Boards?

Green Printed PCB without components.
It is possible to recycle PCB boards, but you will not get everything back. The primary materials in PCB are copper and FR-4. You can use this copper as an electrical conductor.
However, you can only obtain pure copper as the fiberglass will degrade in the recycling process. Still, fiberglass is essential in several low-tech applications.
Here are the ways to recycle PCB:
Thermal Recovering
As the name suggests, the technique involves subjecting the PCB to high temperatures.
Primarily, it's handy in the recovery of metals as the FR-4 cannot survive high temperatures.
Also, it's easy to implement, but it releases hazardous fumes of lead and dioxin.
Chemical Recovering
Firstly, you need to place the PCB in a bed of acid. The acid solution will digest the FR-4, making it impossible to recover.
Like the technique mentioned above, you can only contain metals from this recovery process.
Also, the process will release wastewater which you can reuse after treatment.
Computer parts ready for recycling.
Physical Recovering
It involves the physical separation of metals from nonmetals. Primarily, this is via first smashing and shredding the PCB. Recycling wasted printed materials using this process is safe as it doesn't contribute to environmental pollution.
However, it has several hazards for the operators. First, the machine involved is extremely noisy.
Secondly, it emits dust particles laden with heavy metals and other intoxicants. Lastly, the high temperature causes the PCB to produce an irritant odor.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Circuit Board Recycling Process

Printed circuit board with components
The primary process involves cutting and sorting the PCB components via the following steps.
- First, you need to remove the components attached to the green boards via drilling.
- Next, cut the PCB board into tiny pieces.
- Also, you need to separate ferromagnetic materials from non-ferrous metals. Thus, you'll require magnetic separators to isolate the non-magnetic waste.
- Lastly, you need to sort out other materials such as ceramics and fiberglass.
After cutting and sorting, companies in the recycling industry use three main procedures.
Electronic Waste
Pyrometallurgy
Pyrometallurgical processes involve heating the PCB to approximately 1400 to 1600 degrees. Subsequently, metals such as lead, tin, and oxides will change to a liquid slurry. Additionally, the heating will change organic materials to hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Hydrometallurgy
First, you need to dissolve the PCB in a solution of aqueous leaching agents. Next, you need to add a precipitation agent to convert the slurry from liquid to solid waste. Lastly, add the materials to an ion exchange system to remove the metal ions.
Electrochemical Process
Primarily, this procedure involves the separation of precious metals via electrolysis from the waste stream.
What You Can Recycle from Printed Circuit Boards
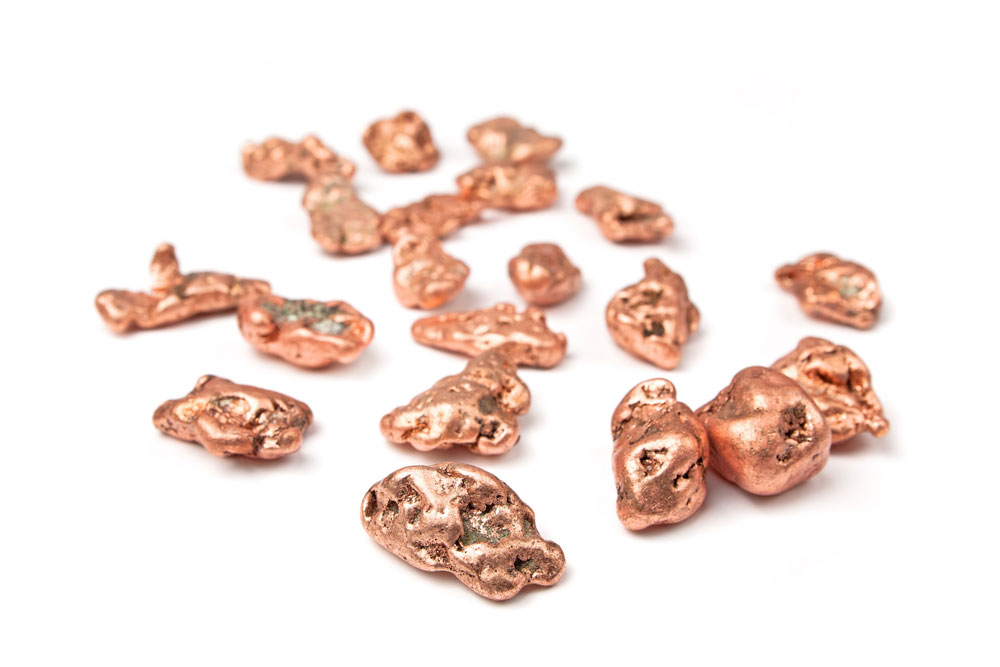

Copper is the main product recovered from PCBs.
Essentially, recycling aims to acquire as many metal scraps as possible. The precious primary materials that you'll recover are copper and tin. You'll obtain copper from:
- Treatment sludge
- Edge trim
- Etching solution
- Rack stripping
- Solder stripping
Furthermore, in the extraction of copper, you can also obtain copper hydroxide, specifically in the hole process.
Lastly, you can generate tin during the hot air leveling procedure.
What Parts of the Circuit Board Are Worth Money?
When you consider an assembled board, the most valuable parts begin with the mounted components if fully functional.
Integrated circuits like microprocessors and microcontrollers are most valuable in this lot, and once you remove all components, the metals that make up the board are next in line.
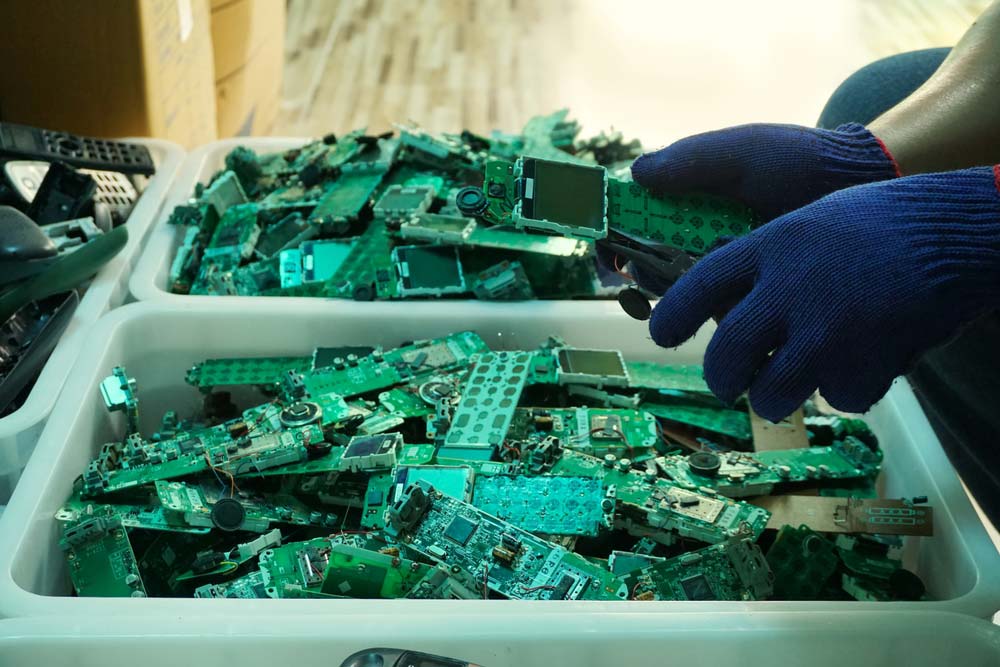

Phone PCBAs being disassembled in a recycling plant
Copper is the most prevalent metal because it makes up the circuit connections, and the quantity is more if the board contains multiple layers.
Some PCBs also have tiny amounts of valuable metals like gold, silver, nickel, and palladium. But their value depends on the quantity and purity.
Substrate materials like fiberglass have the least value in the PCB structure.
Can You Make Money From Recycling Circuit Boards?
Out of an entire PCB, the metallic components form the lion’s share, taking about 40% of the materials. Plastics and inert oxides follow suit with 30% each.
So, the primary function of PCB recycling is to recover the metal materials because they are the majority and most valuable.
Of this metal composition, copper takes the largest share at 20%, followed by iron at 8%, tin at 4%, and zinc & nickel at 2% each.
Precious metals like silver, gold, and palladium take up 0.2%, 0.1%, and 0.005%, respectively.
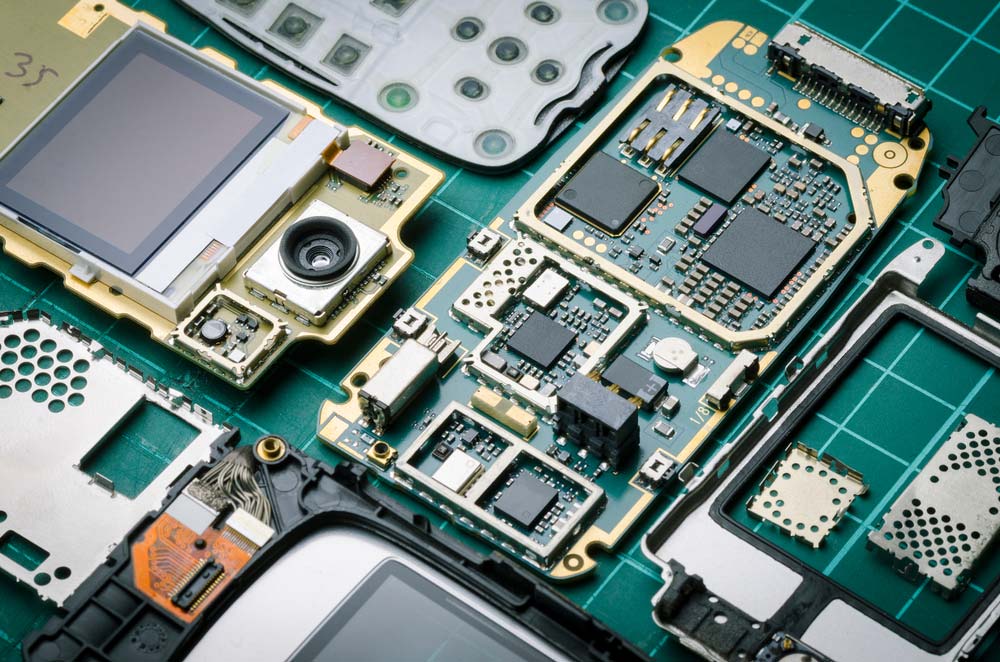

An old phone’s PCB with valuable parts like semiconductors and gold surface finishes
Therefore, the most significant earners when selling recycled materials are copper and iron.
Copper currently retails at around $8,340 per tonne, while iron goes for around $136 per tonne.
When you add up the prices of the other materials, including resin and fiberglass (sold as filling materials or additives), you can make about $145 per tonne of recycled circuit boards after deducting the total recycling costs.
So, to answer the question, you can make money from recycling PCBs. It's not that much, but it's better than polluting the environment.
Can PCB Recycling Processes Harm the Environment?
There are two ways to look at this PCB recycling process. The first is the intention of it, which is to prevent e-waste from contaminating the earth and water bodies. This is a good thing.
But the second one is not good. The recycling process requires lots of energy to heat and melt some materials (especially metals) to separate them.
Acquiring this energy can pollute the environment if it comes from unclean sources.
Worse still, the materials can release toxic dust or smoke when heated during extraction, which is devastating for the environment.

A PCB with multiple ferrite coils assembled on it
Ideally, companies engaging in pyrometallurgy should invest in the required equipment to heat and recycle the metals in PCBs without polluting the environment.
But the reality on the ground is these boards end up being sent to recyclers in countries where there are less strict regulations to prevent environmental pollution.
So, the low-tech heating methods employed by these recycling companies end up damaging the environment when extracting metals from old boards. Some can even pollute water bodies if they engage in hydrometallurgy.
How to Make PCBs More Recyclable?
A PCB board without components
There is an ever-increasing number of PCBs in the electronics industry. Thus, we need to recycle more waste electrical materials. However, at the moment, there's little that we can do to improve PCB recyclability.
Earlier, there was a notion that using SMD components in place of THT could improve PCB recyclability. Nonetheless, this has proven to be ineffective.
Back to Top: PCB Recycling
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!