IPC standards are something you can't avoid as a reliable PCB producer. In other words, you can't boast of producing reliable PCBs without verifying the IPC standards.
That's why there are a ton of IPC standards to ensure that your product is sturdy.
So, if you're new to PCB design, it's essential to consider the IPC standards. But there's a possibility that you may face some bottlenecks along the way.
That's why we created this article to help you understand IPC standards. Plus, we made it very simple and easy to understand. Hence, you don't have to worry because we've got you covered.
So, if you're ready, let's kick start!
Contents
- What Are IPC standards?
- The IPC Standards
- What does the IPC Body Do (In Detail)?
- Where Do You Get IPC Standard Products?
- A Brief History of IPC Standards (How It All Started)
- IPC Standards for PCB Design and Production Processes
- IPC-2221
- IPC-2222
- IPC-2152
- IPC-4101
- IPC-4761
- IPC-2581
- IPC-6011
- IPC-6012
- IPC-7351
- IPC-1752A
- IPC-A-600
- IPC-A-610
- IPC-A-620
- IPC-A-630
- IPC-J-STD-001
- IPC-TM-650
- IPC-7711/IPC-7721
- IPC-1752
- Classifications and Terms Used in IPC Standards
- Classes of Electronics Based on IPC Standards
- Additional Terms Used in IPC Standard
- Acceptance tests
- Assembly
- Critical Operation
- Integrated Circuit
- Resist
- Flexural Strength
- Common Defects of IPC PCBs
- Annular Ring
- Short Circuits
- Open Solder Joints
- Component Shifting
- Why Is IPC Standards Important in PCB Production?
- Improved Product Quality and Reliability
- Improved Communication
- Reduced Costs
- Maintains Consistency
- Retains the Reputation
- How To Choose The Right IPC Class Standard
- Use Case
- Cost
- Application
- Other Important Industry Standards for Electronics
- ISO
- IEC
- UL
- RoHS
- MIL-PRF
- MIL-STD
- Closing Words
What Are IPC standards?
Before we dive into the topic, let's look at the definition of IP standards.
First, we can't define IPC standards without understanding "IPC."
So, IPC is a global body. And it enables producers to build quality electronics backed up by proven standards.
But there's more.
Hence, these producers are certified, educated, and informed by IPC so that they don't deviate from IPC standards.
Also, IPC provides public policy advocacy and market research for the producers.
So, here's the kicker.
IPC has over 4,800 member companies across the world. Plus, these members get governed by the policies of the body.
Also, the members come from every aspect of the electronics industry.
So, we see electronics, suppliers, designers, and PCB producers under the body. Following established PCB design guidelines and best practices can help stakeholders align their processes with IPC standards for quality and efficiency.
But that's not all.
Authentic equipment producers and assembly firms are part of IPC.
In the end, no stakeholder in the electronics industry is missing.
The body also has its headquarters in Bannockburn, Illinois, United States, and other office branches within the United States.
Other countries like China, India, Russia, and Sweden have IPC offices as well.
But there's more.
IPC got accreditation from the ANSI. Afterward, they got certified as a standard-developing organization.
The IPC Standards
So, we'll be going in-depth on IPC standards since we now understand IPC.
The IPC standards are acceptable codes in the electronics industry. The body also publishes standard codes for all phases of production.
Hence, you'll find these codes in stages like design, assembly, packaging, etc.
By the way, IPC has over 300 operational standards and over 1,000 standards in its library.
Furthermore, a committee of volunteers is responsible for the IPC codes. For the most part, the committee drafts, modifies and creates the IPC standards.
As a result, over 3,000 electronics professionals participate in the process. Committee members can include people from all over the world, so members participate via email, in-person, or teleconference.
What does the IPC Body Do (In Detail)?
First, the IPC body offers validation service programs. And they have a standards gap analysis team. So, they use their means to help producers address their production challenges. Furthermore, the body enlightens the producers on things to do to meet quality standards.
But that's not all.
The body also maintains a list of qualified producers. In short, they create it to help the public discover products that meet the IPC standards.
Besides, the association has over 110 IPC-licensed training hubs globally. Also, the body provides multimedia & online training and education resources. Plus, they host informative events, management, and technical conferences. To summarize, IPC APEX EXPO is the largest exhibition show in the US. South China is responsible for APEX, which is IPC's as well.
Also, the IPC body carries out loads of market research. Plus, they do a lot of work in environmental policy and government relations.
In conclusion, IPC is a great advocate for the electronics industry globally. And they have regulators across the globe.
Where Do You Get IPC Standard Products?
So, we must be frank with you. IPC standard products aren't free. Therefore, don't expect to get them without spending a dime.
However, you can still get a rebate when you buy from the IPC store as a member. Also, they have loads of IPC stores you can patronize. Hence, an excellent example of a verified IPC store is ourpcb.com.
A Brief History of IPC Standards (How It All Started)
In 1957, IPC began as the Institute for Printed Circuits. Then, six printed circuit board producers formed the body. Later, in 1958, IPC created and published its first book. At that time, the book sold up to 25,000 copies. So the name of the book is "How to Design and Specify Printed Circuits."

Source: ipc.org
Next, in 1964, IPC published the pioneer version of the IPC-A-600. Thus, the body called the standard the Acceptability of Printed Boards.
By the way, this standard is STILL the primary source of visual support for bare board acceptability.
And all the requirements are in the IPC-6010 series. Also, the IPC has updated and revised the series. And they have done it seven times since 1964.
Later, the body changed its name to the Institute for Interconnecting and Packaging Electronic Circuits. This name change happened in 1977, and it was due to the large number of electronic assembly firms that joined the body.
By 1998, the body decided to stick to IPC as its official name. This happened because many people couldn't memorize the full name.
Plus, there was another set of people who disagreed with the meaning of the words in the name.
Thus, the association made IPC the central name. But that wasn't all. They got a tagline that says, "Association Connecting Electronics Industries."
Source: ipc.org
IPC Standards for PCB Design and Production Processes
IPC-2221
This generic PCB design and performance requirement standard covers several aspects, such as PCB design requirements, thermal management, material requirements (substrates, plating, etc.), and annular rings, among many others.
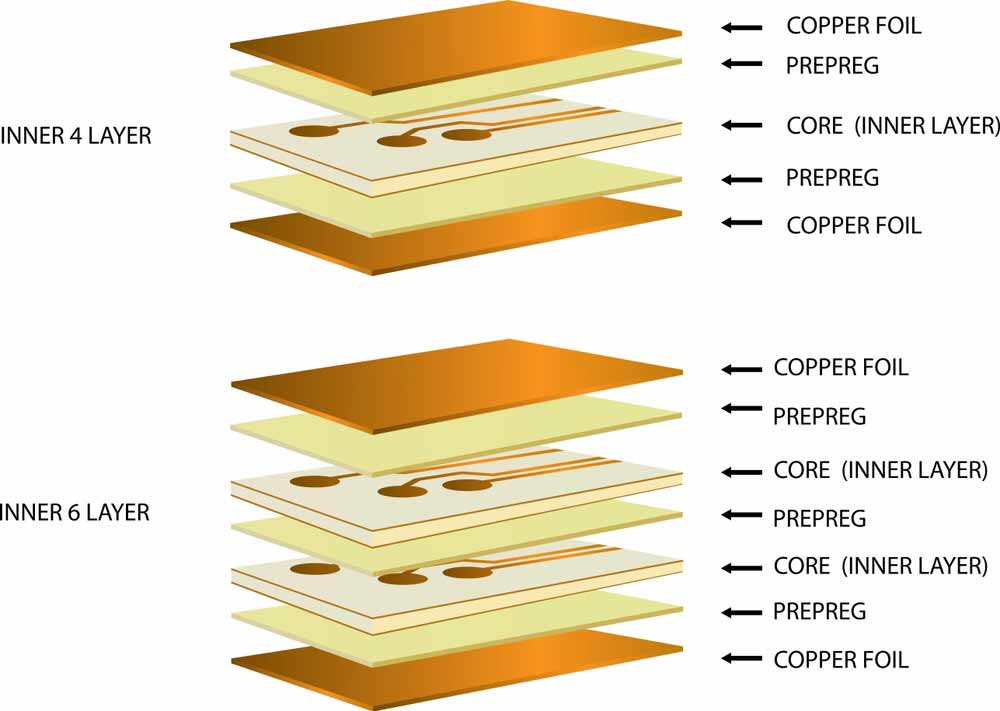
PCB layers and materials
IPC-2222
The IPC-2222 standard, which establishes the criteria or requirements for designing rigid organic circuit boards, interconnecting structures, and other forms of component mounting, is usually used in conjunction with 2221.
IPC-2152
IPC-2152 is relatively new because it improves on the IPC-2221 standard to optimize the conductor size. It determines the current-carrying capacity of the copper transmission lines and planes, trace width, and temperature rise when conducting.
IPC-4101
This standard primarily applies to rigid and multilayer boards, and it covers the requirements for substrate selection, as well as prepregs and laminates.
IPC-4761
IPC-4761 looks at the via-hole protection guidelines to ensure they are high-quality, manufacturable, and reliable.
IPC-2581
Also known as IPC-DPMX (Digital Product Model Exchange), this standard comes into play when exchanging data between the PCB designer and manufacturer. It provides a standardized format for exchanging this PCB design data to ensure uniformity and consistency in production.
IPC-6011
This guideline covers the general performance specifications for PCBs and outlines the reliability and quality levels they must meet during design, assembly, inspection, and testing.

PCB inspection for the automotive industry
IPC-6012
The body named this standard the quality and performance specification for rigid PCBs. In other words, the IPC-6012 forms the criterion and performance for rigid boards.
So, the specifications apply to a single side & multiple boards. It is also ideal for metalcore printed boards. Plus, active or passive embedded circuity printed boards aren't left out.
IPC-7351
IPC-7351 specifies the circuit board’s footprint and land pattern for the surface mount pads, including optimum shape, size, and tolerance. Electronic component manufacturers usually use this standard to maximize solderability and create reliable electrical joints.
IPC-1752A
This material declaration data exchange standard defines the reporting formats for the information exchanged between PCB designers, distributors, and manufacturers.
IPC-A-600
Like we earlier mentioned, IPC-A-600 is the acceptability of printed boards. It's also known as IPC-600. This standard creates a criterion for every product class. Also, it defines the necessary and perfect conditions for every PCB.
IPC-A-610
The IPC-A-610 standard is the acceptability of electronic assemblies. Hence, it creates the criterion for end-product acceptance. Plus, it's one of the most popular standards used by the IPC body.
IPC-A-620
IPC-A-620 gives acceptable practices and requirements for manufacturing cables, wires, and wire harness assemblies, which you can use to interconnect PCBs.
IPC-A-630
This acceptability standard defines what is acceptable during the manufacturing, testing, and inspection of electronic enclosures.
IPC-J-STD-001
This standard describes the criteria required to produce quality soldered interconnections. Also, it tells the method and material involved in the process. In short, the standard focuses on process control. And it sets requirements for electronic products.
IPC-TM-650
This document provides the testing procedures for evaluating various PCB guidelines, such as the power density rating for embedded resistive components.
IPC-7711/IPC-7721
This standard is responsible for the rework of electronic assemblies or repairs. It also monitors the modification of PCB and electronic assemblies.
IPC-1752
IPC-1752 defines the substance disclosure requirements outlined in the latest JIG-101 version.
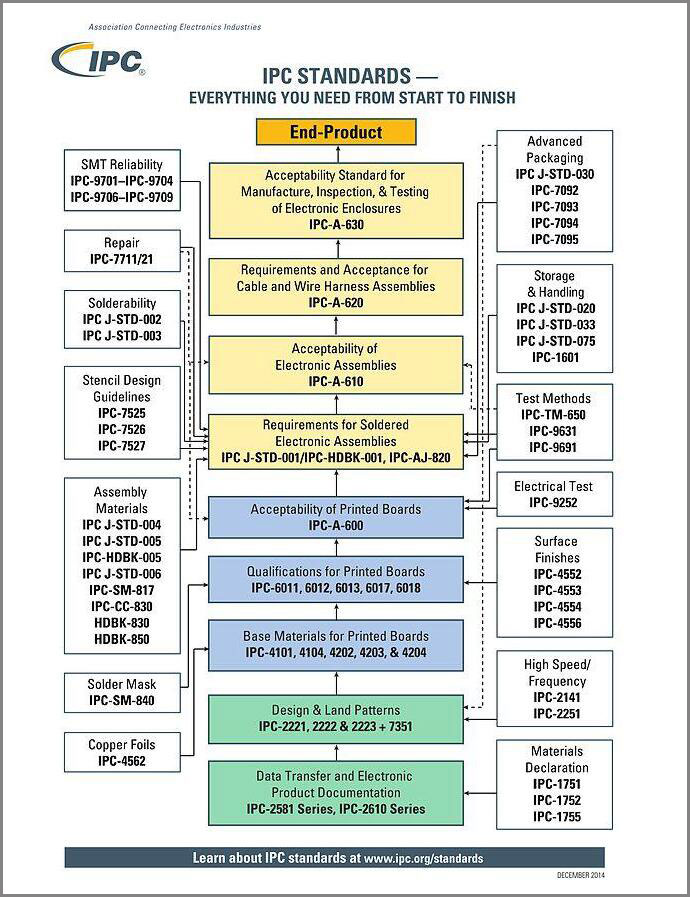
Source:ipc.org
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Classifications and Terms Used in IPC Standards
It’s vital to pay attention to IPC terms.
Why?
It’s because each word means different things. Plus, it comes with two selected terms. So, you’ll find these terms in the IPC-A-620 standard.
They are:
Must or shall: if you see any of these terms, it means one thing. The requirement discussed is compulsory. Thus, it applies to all product classes.
Should: this word shows recommendation. Also, it’s useful for reflecting procedures. Besides, it’s ideal for general industry practices for guidance.
Now you understand the terms used in IPC standards, so let’s proceed to the classes.
Classes of Electronics Based on IPC Standards
When it comes to electronics production, PCBs are in three classes. Hence, each category shows the quality of the circuit board.
So, the classes are:
IPC Class 1 – General Electronic Products
Class one is where you find every day general electronics products.
Besides, the products in this class have boards. Plus, they have the lowest quality requirement. Therefore, they usually have a short life cycle.
However, there’s more.
The primary requirement of class one products is the function quality. Thus, the end-product operation is more crucial.
Also, it’s one of the most lenient classes. That’s why it allows for potential defects. So, a great example of its products are smartphones, toys, etc.
IPC Class 2 – Dedicated Service Electronic Products
Class two are electronics long life-cycle and continued performance. Also, class two products require uninterrupted service. So, producers ensure the products don’t fail during operation.
In other words, products in this category are acceptable. Plus, they have a long life cycle. So, a good tip here is to know the class you want. Afterward, you can pursue the board designs.
That way, you can easily design your products for a specific class. Examples of products in this category are microwave, televisions, etc.
IPC Class 3 – High-Performance Electronic Products
IPC class three consists of electronics that are mission-critical. In other words, class 3 electronic products use circuit boards. Plus, they follow strict guidelines.
So, the IPC class three products are high-reliability electronics. Also, they have a long life cycle with fail-proof quality. So, examples of its products are military radar, pacemakers, etc.
Additional Terms Used in IPC Standard
Here are additional ones you may like to know. They are:
Acceptance tests
An acceptance test helps you to know if a product is acceptable. Plus, a vendor or a buyer must agree with it.
Assembly
Assembly is the joining of several parts or subassemblies.
Critical Operation
A critical operation is a procedure of an entire process. So, it usually has a massive impact on the quality of the finished product.
Integrated Circuit
This term refers to a combination of electronic components. It’s also known as or a microchip. Usually, they fabricate it as a single unit. By doing so, it produces a microcircuit function.
Resist
Resist is a coating material. Hence, its function is to protect certain areas of a pattern. Also, it’s better during testing or production.
Flexural Strength
Flexural strength is also called bend strength. Also, it’s the resistance of a material against deformation.
Besides, here’s the kicker.
The flexural strength shows you something vital. It shows the needed force to break a test sample. Plus, it must be of a specific diameter before it works.
Common Defects of IPC PCBs
Annular Ring
An annular ring can unintentionally turn the via-hole drilled between a pad into a covered pad. Some defects, like a 90° disconnection on the ring, are acceptable under class 2 because these do not affect the board’s performance. But a covered annular ring is unacceptable.
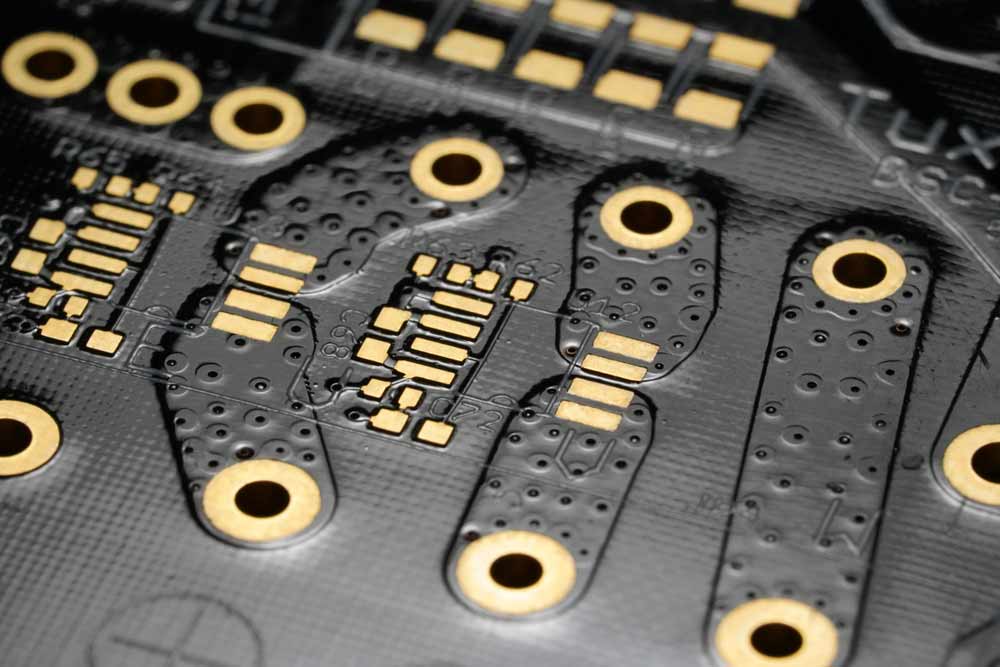
Annular rings on a PCB
Short Circuits
Shorts resulting from solder bridging can also occur and cause serious damage to the circuit or components. Some can be microscopic, making them difficult to spot and these are the most dangerous because the PCB might pass the tests with this error undetected.
Open Solder Joints
This fault occurs when there is a weak integral bond between the component pin or lead and the solder pad. The open joint can cause arcing or discontinuity and it occurs when solder only appears on the pad but not on the component pin or vice versa.
Component Shifting
Component shifting can only occur when the solder is hot and liquid, which allows components with multiple pins, like BGA chips, to realign. You should ensure such components are in the middle of the pad or land area, which should keep the pins connected to the right pad at least until the solder solidifies.
Why Is IPC Standards Important in PCB Production?
IPC standards keep producers in check. That is, it helps them build reliable and safe PCB boards.
How?
Producers pay attention to the details of the production standards. That way, they maintain quality throughout the process. Thus, they improve the production process. And by doing so, they meet customers’ expectations.
The IPC standard also supports producers in the following ways:
Improved Product Quality and Reliability
IPC standards take effect from the beginning of the production process. So, it means one thing. The final product will perform better and last longer. Also, this translates to high quality and reliability.
Improved Communication
With IPC standards, the same language flows in and out. As a result, there’s a reduced risk of miscommunication. So, people can’t mix up the terminologies. Plus, they can easily detect the life cycle of an electronic device.
Reduced Costs
If producers follow IPC standards, they won’t need to do quality checks. So, it helps to reduce the testing cost.
Maintains Consistency
It’s quite tricky for producers to maintain consistency in quality. But, it’s perfect when they follow and maintain IPC certification. That way, the products can maintain quality. Also, the producer can boost their customers’ satisfaction with consistency.
Retains the Reputation
Engineers in the electronic industry are familiar with IPC standards. And it’s because IPC is internationally recognized.
So here’s the thing.
Even newly employed staff can maintain your reputation. Why? It’s because there are standards to follow.
How To Choose The Right IPC Class Standard
Use Case
The PCB supply chain has different actors, beginning with the designer. These personnel can only adhere to specific IPC standards, such as 2221, while manufacturers should strictly adhere to IPC-6011. IPC-1752A applies to all, so they share it to optimize cooperation.

A PCB designer at work
Cost
IPC falls into classes 1, 2, and 3, with the highest level (class 3) having the strictest quality inspection guidelines. Implementing standards in this class will be costly because the electronic product might need expensive, high-performance materials or processes.
Application
The final device's application also determines the standard class to use. For instance, consumer electronics generally fall in class 2, but devices for military, space, satellite, and other demanding applications require class 3 implementation.
Other Important Industry Standards for Electronics
ISO
The International Standards Organization primarily covers international standards for product manufacturing and quality control. Typical ISO standards used in the electronics industry are ISO 9000, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 13485 (for medical devices).
IEC
The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is an organization that emphasizes international cooperation in developing electrical and electronic safety and performance standards.
UL
Underwriters Laboratory is an international testing and certification organization that develops safety, sustainability, and quality standards. To date, the organization has published more than 1800 standards.
RoHS
Also known as directive 2002/95/EC, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) was brought to life by an EU legislation that bans the use of specific materials in PCB manufacturing.
RoHS standardizes the materials and processes of making electronic products with the goal of making them safer for the environment and human health.
MIL-PRF
MIL-PRF is an acronym for military performance specification, and it applies reliability and mechanical performance standards to defense and military electronic equipment.
MIL-STD
MIL-STD, or military standards, is a broad set of standards that applies to military hardware. These standards define the hardware and testing requirements.
Closing Words
We can't stress the IPC standards. Plus, there are necessities every PCB producer needs to meet the standards.
So, if you're into PCB production, you always need to meet the IP standards.
Meeting these standards would also benefit you. You'd boost brand trust, which would result in more customers patronizing your firm.
So, if you want to get more clarification about this topic, feel free to reach us.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!