As a budding computer hardware engineer you may be asking yourself questions like, "what does DC voltage mean?" and "what does direct current mean?". This type of current that serves an essential function as power outlets in the home and commercial space can be a mystery if you're not clued up on what voltage or current is — luckily, that's where OurPCB comes in.
Our team has written this comprehensive guide to provide an in-depth look at everything DC voltage and current so you can understand your PC, outlet, or science project better.
Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What Is DC Current and Volt DC?
- What Is the Symbol for Direct Current?
- How Do I Measure the DC?
- How To Calculate DC Power?
- Step 1:
- What Is The Difference Between AC and DC?
- What are the Applications of Direct Current?
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of DC?
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- DC Voltage FAQs
- What Blocks DC Voltage?
- Is DC Safer Than AC?
Key Takeaways
- DC voltage is a constant voltage that moves the direction of the current in a single direction.
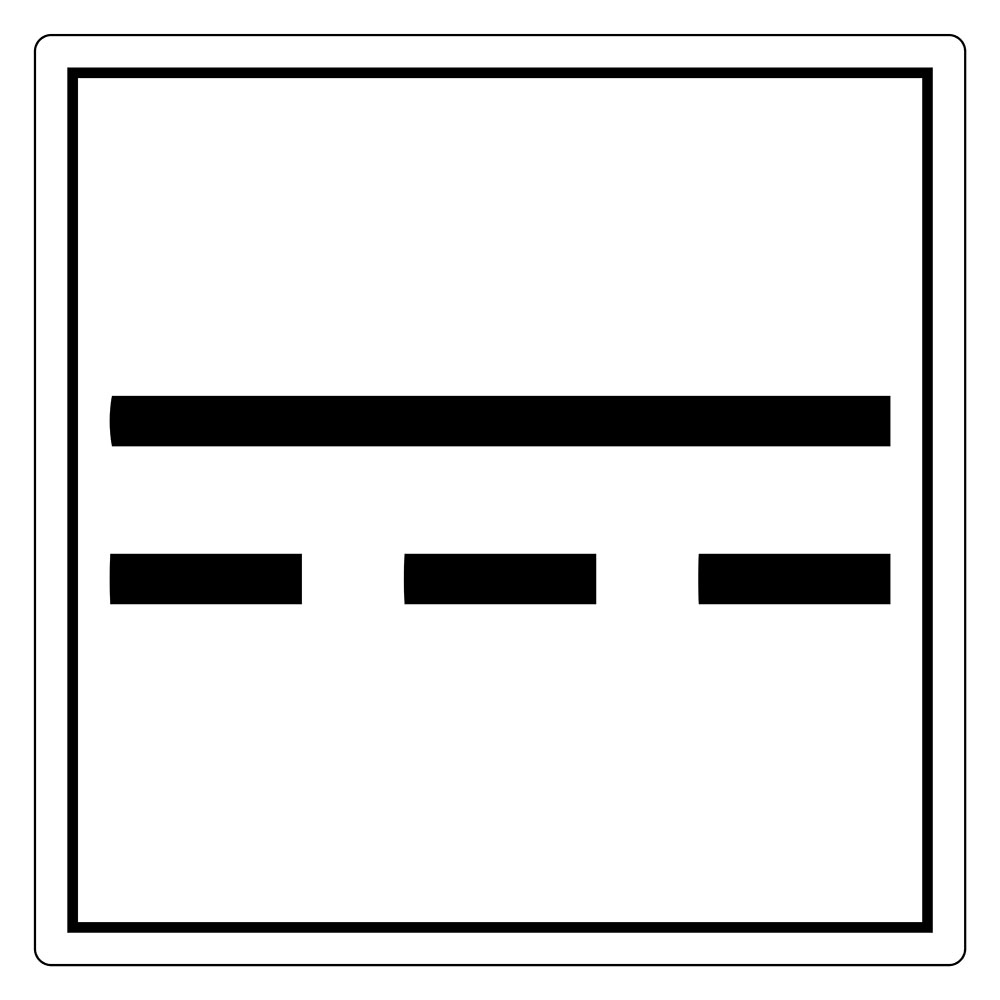
- The symbol for DC (-) is a straight line, similar to a minus or dash.
- The easiest way to measure voltage across your circuit is using a digital multimeter. You can also calculate it using Ohm's Law if you have the resistance and current.
- The difference between DC and AC is that DC moves unidirectionally, while AC will move in both directions.
- DC voltage is used in solar cells, thermocouples, batteries, as well as fuel cells
What Is DC Current and Volt DC?
The DC in voltage and current stands for “direct current” or “constant polarity”. A DC voltage is a constant voltage that drives the current in one direction. This means the current flows in one direction. However, it can vary in time. Rectifiers, solar panels, as well as batteries all, produce DC voltage from a chemical reaction.
A voltmeter measures the DC voltage levels. There are also several DC voltage power sources in use. For instance, most logic circuits, flashlights, trucks, and cars use a DC power supply. DC flow of current is present in anything. Meanwhile, the electric charge in DC has one direction of flow.
Furthermore, most digital electronic devices use DC electrical power. DC, in fact, converts the chemical energy in a battery to electrical energy. It also moves electrons from the point of negative charge to positive control without changing direction.
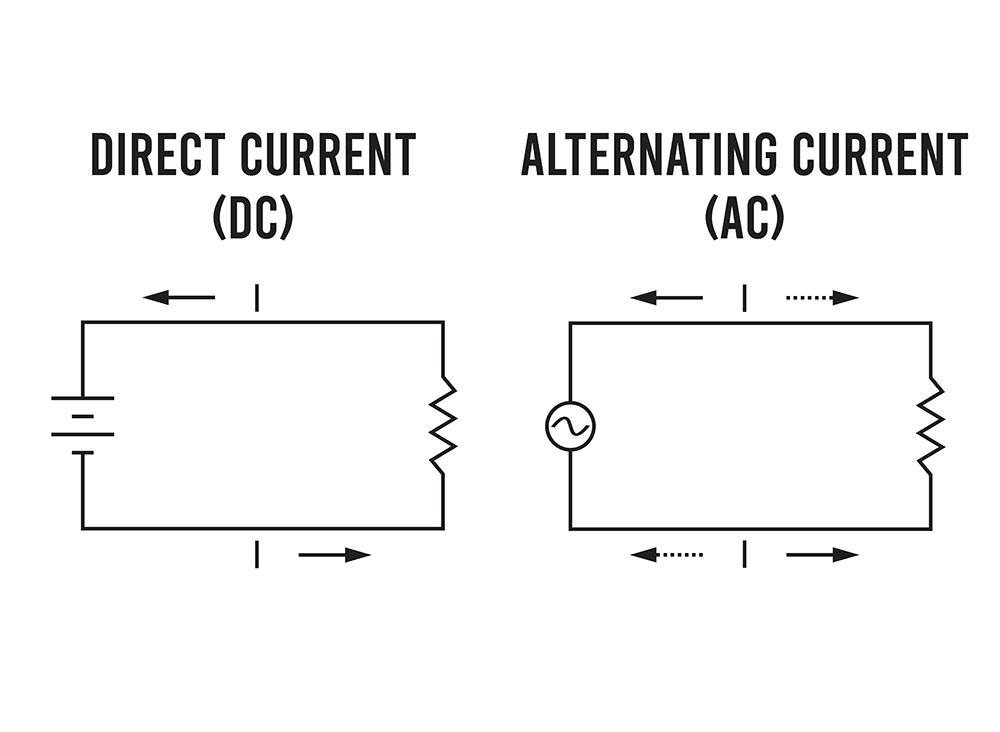
What Is the Symbol for Direct Current?
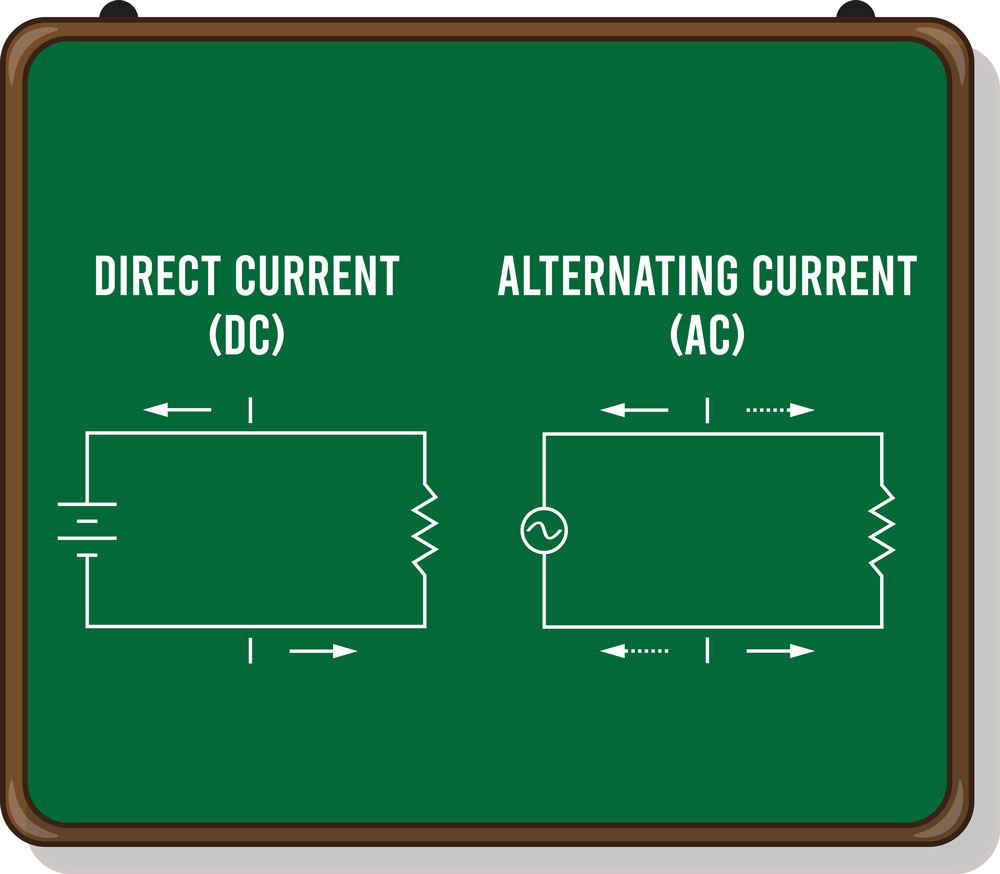
Since DC is constant, the symbol is a straight line. A straight line certainly means that the current is unidirectional. The figure below shows an illustration of the DC circuit.
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
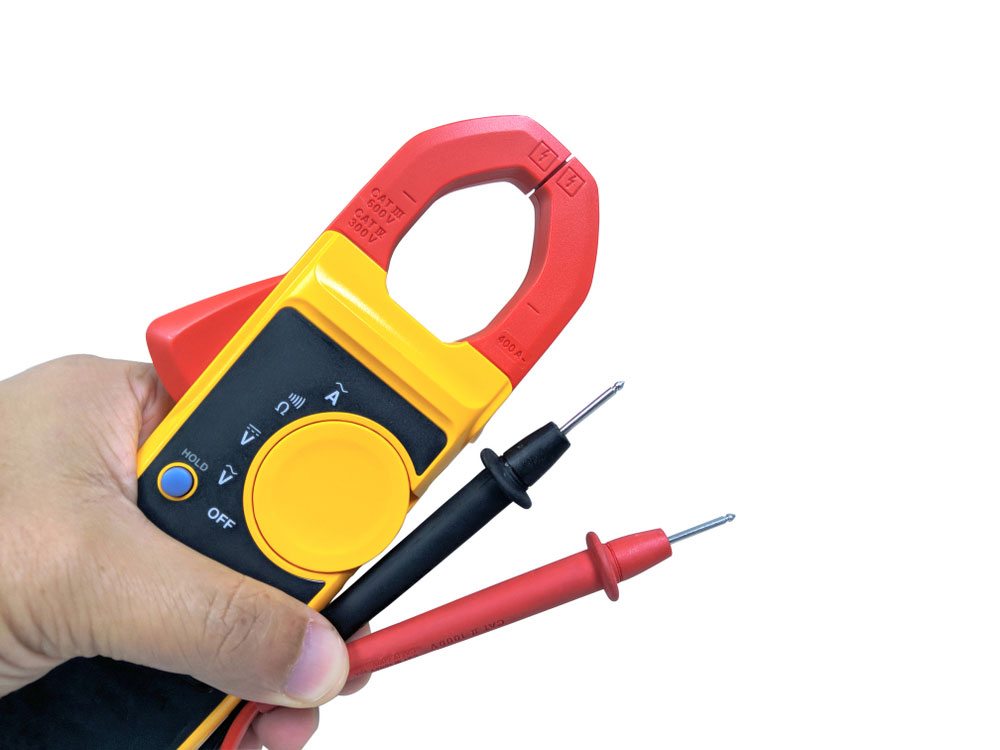
How Do I Measure the DC?
The simplest way to measure a DC is with a digital multimeter. Current measurements are often easy to take. Below are simple steps on how to measure DC:
- Firstly, connect the black probe of the multimeter into the COM Jack.
- Then, put the red probes in the V Jack. After this, in reverse order, remove the red probe first, then the black searchlight black probe should connect to the negative polarity circuit ground and the red search to the positive test point.
- Put the type of DC in the multimeter and read the measurement on display.
Another way to measure the DC flow of charge through a conductor is by using a clamp-on-meter.

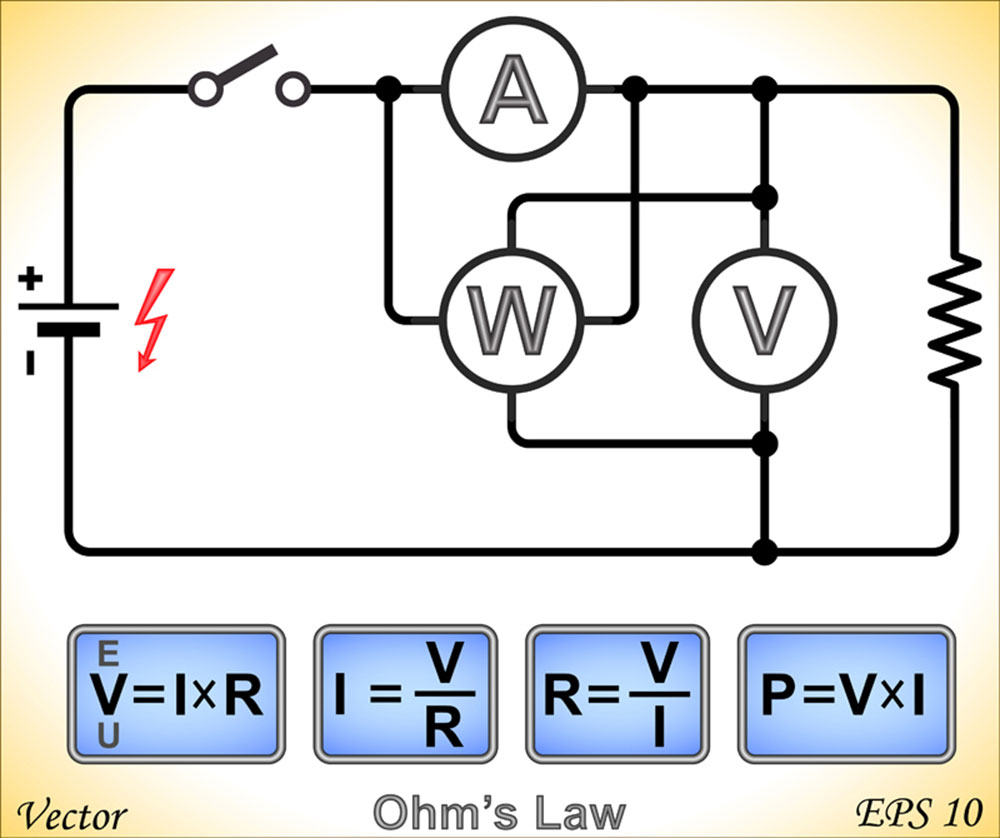
How To Calculate DC Power?
You can calculate the power of a DC electrical system using Ohm's Law as long as you have the current, resistance, and voltage of your direct current electricity circuit. Here's how you can do it step-by-step:
Step 1:
Using ohm's law, you can specifically calculate the current (l), resistance ®, and voltage (V) of a DC circuit. With the result, you can then subsequently calculate the output power at any point in the circuit. Ohm's law formula is Voltage (V) equals Current (I) times Resistance (R).
V = I x R
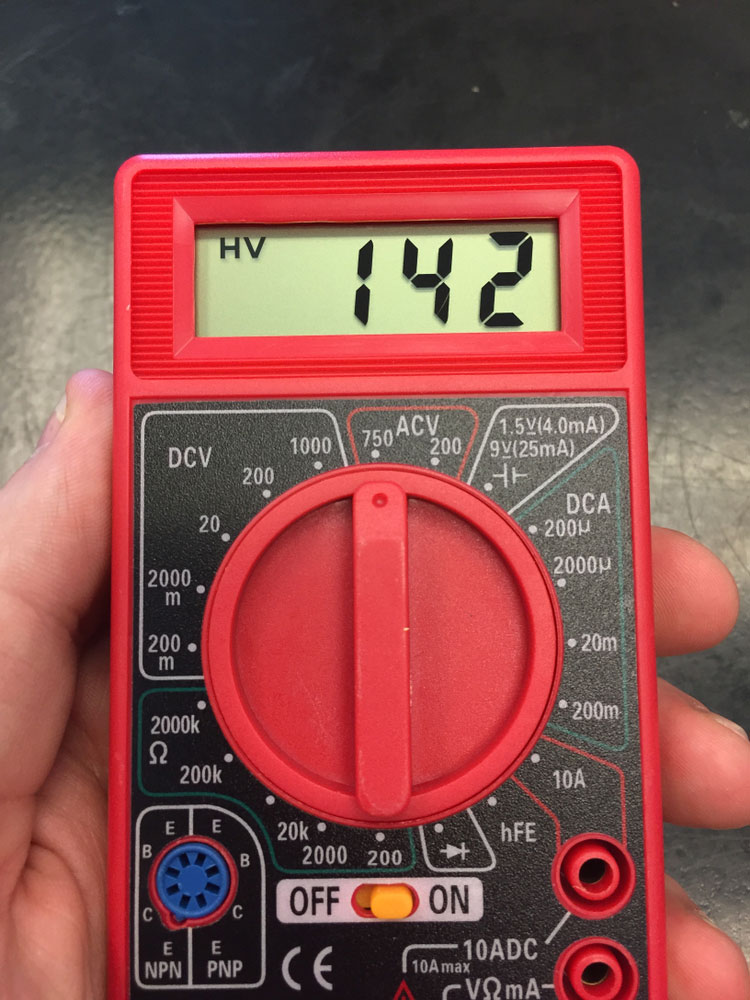

For example, if current (I) is 0.6 amps - DC (600 milliamps), R is 150 ohms. Using the formula above to calculate the maximum voltage: 0.6 x 150 = 90 volts. Moreover, in a situation, resistance measurement is unavailable, and it’s ideal to use the 4-wire mode measurement timing for accurate precision.
Step 2:
To calculate DC power: Power (watts) = Voltage (volts) x Current (amps).
P = V x I
From step 1, P = 90 x 0.6 A = 54W.
What Is The Difference Between AC and DC?
The main difference between AC and DC is that DC currents move in one direction, while AC will reverse its direction. Electrical energy comes in two forms: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Both powers are essential for the functioning of all electrical devices. However, these forms of energy differ in application, signals, mode, amongst other things.
The significant difference between AC and DC power, and it’s in the comparison chart below;
| Direct current (DC) | Alternating current (AC) | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | The frequency of the direct current is 0 Hertz (Hz). Since DC doesn't move in a waveform like AC, it has zero frequency because it has a unidirectional flow. | The frequency of AC shows how many times it reverses its direction. For example, the most popular AC frequency is 60 cycles per second, commonly known as 60 Hertz (Hz). So if the frequency is 55 Hertz, the current changes direction 55 times. |
| The direction of current flow | When a direct current flows through a circuit, it never changes direction in particular. | When alternating current flows through a circuit, it periodically reverses direction. In like manner, it also creates a spinning wire loop in a magnetic field. |
| Electron motion | The electrons surely move in a fixed direction without changing. | The electrons flow back and forth in an alternating direction. |
| Current size | The DC remains a constant magnitude for time. However, with a pulsating DC, it has a varying extent. | The magnitude of AC particularly varies continuously concerning time. |
| Passive parameter | Only resistance. | >Impedance. This includes both reactance and resistance. |
| The Power factor | It is invariably 1. | It falls between 0 to 1. |
| Conversion | DC is usually converted to AC with a rectifier. | AC converts to DC by using an inverter. |
| Type | DC is often classified into pulsating and pure DC. | Sinusoidal, Square, Trapezoidal, and a Triangle wave. |
| Waveform | It has no waveform. | AC waveform truly alternates. The waves form when alternators at power plants make AC power. |
| The load type | It only connects with the resistive type of load. | On the contrary, Ac voltage connects with the capacitive, inductive, and resistive types of load. |
| Hazardous | DC electrical power is more hazardous compared to AC for a similar rating. | When handled carelessly, it is undoubtedly hazardous. |
| Application | Cell phones, Flat-screen TVs, Flashlights, electric and hybrid vehicles, etc. | Household and industrial appliances like dishwashers, refrigerators, and toasting machines use AC. |
| Source | It uses both a DC battery and a generator. | On the other hand, it uses an AC circuit and generator. |
| Electrical energy transmission | In power or electrical sources, the most current transmission system is through an HVDC. Besides, In this system, DC has a low voltage loss. | It is also transmittable through the HVDC. |
| Efficiency | Super efficient | It has low efficiency. |
| Sweep types | This current source mode usually calculates the circuit bias point of selected power sources in predefined stages over a range of voltage values. Additionally, DC sweep also works alongside any source that has a DC variable. | AC sweep simulation is specifically for calculating the small-signal response of a circuit voltage. |
| Scan type | The scan speed is between 100 ms and 10,000 s. It also functions in a ramp or triangle wave. | This scan type ordinarily performs an at-speed sample cycle to ascertain timing compliance. |
What are the Applications of Direct Current?
Presently, DC source modes are solar cells, thermocouples, batteries, as well as fuel cells. Unlike AC which is the best pick for power plants and the electrical grid, various applications use this common type of power.
Additionally, DC primarily functions in all consumer electronics. It is helpful in several applications like Cell phones, Flat-screen TVs, LED lights, electric and hybrid vehicles. Furthermore, it mainly works in applications with low volts, such as aircraft and charging batteries. Most energy mass storage devices are also DC-based.
Direct current also transmits electricity with greater efficiency over a vast distance. DC applications and technology are not only very reliable, but they last for hours. Besides, in the PV industry, DC power supplies off-grid appliances and portable solar systems electric energy. The direct high-voltage current (HVDC) also uses DC to transmit electricity to bulk power systems like wind turbines.

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of DC?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Constant Voltage. Maintains a steady voltage level, ideal for electronics and sensitive devices. | Transmission Losses. Suffers higher energy losses over long distances compared to AC transmission systems. |
| Energy Efficiency. Experiences less energy loss in specific applications, such as short-distance transmission. | Conversion Challenges. Requires complex and expensive converters to switch between AC and DC systems. |
| Energy Storage Compatibility. Easily stored in batteries, making DC essential for portable and renewable energy systems. | Infrastructure Limitations. Less established infrastructure for DC distribution compared to widespread AC networks. |
| Compatibility with Electronics. Most electronic devices operate on DC, simplifying power supply requirements. | Voltage Transformation. More difficult to efficiently transform DC voltages to different levels. |
| Easier Control and Regulation. Allows for precise control over voltage and current levels, enhancing performance and safety. | Safety Concerns. Poses higher risks of electric shock and arcing at the same voltage levels as AC systems. |
Formerly AC voltage current was often a form of energy suitable for power dissipation. But today, DC is emerging in the technological area. As a result, it can create job opportunities, increase research, inspire innovation, and stimulate economic growth.
The most significant advantage of DC over AC is its ability to perform in particular applications. For example, DC is preferable when there is an AC voltage drop for extended coverages. Listed below are the advantages and disadvantages of DC.
Advantages

- It is easier and faster to change the speed of a DC electric motor.
- DC indeed works in all consumer electronics.
- Stores electric current. Again, DCsaves electricity in mass storage devices and small applications like the rechargeable battery and power banks. By storing electricity, it, in fact, becomes easily accessible when the renewable sources are not providing energy after the daylight hours.
- Better age regulation because the voltage output drop is comparatively tiny.
- The resistance conductive materials are generally very effective.
- Requires less insulation to function because the pressure on the conductor is small.

Disadvantages
- With high-level constant voltage inputs, it becomes difficult to generate DC because of communication problems.
- The DC voltage system is also challenging to increase for high voltage transmission.
- DC circuit voltage and switches are expensive in appliances. Above all, they often have a gear warranty on defects in materials.
- The DC transmission setup is particularly complex.
- You can’t modify direct current voltage input.
We've given a comprehensive overview of DC constant voltage current and its advantages and disadvantages but if you want to understand how basic DC circuit theory can be used to bring your PCB designs ideas to life, then make sure to contact us today.
DC Voltage FAQs
What Blocks DC Voltage?
Blocking DC voltage involves preventing the flow of direct current in a circuit. Various components and materials can achieve this by introducing resistance, creating open circuits, or allowing current to flow only in specific directions including diodes, capacitors, resistors, and insulators.
Is DC Safer Than AC?
Studies show that AC is more dangerous than DC since it interferes with your heart's electrical signals, that can lead to heart issues. DC can still cause the same issues, but requires a higher current to do so (100mA vs 300 to 500mA).
Back to Top: Understanding DC Voltage: Principles and Applications
Special Offer: Get $100 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!