Temperature Sensor is one of the most measured physical properties in the globe. Several industries and applications need to keep tabs on this property to safeguard systems, items under research/ investigation, or the final product. This protection is important because the extremely high or low range of temperatures can cause damage. Thermocouple sensors are the most common sensors used for temperature measurement, and we have covered the device in detail below. Read on to learn more about the sensor's types, working principles, and more!
Contents
- What is a Thermocouple Sensor?
- Thermocouple Types
- How Does A Thermocouple Work?
- Temperature Sensors Comparison: Thermocouples, RTDs, and Thermistors
- Thermocouple vs. Thermopile
- Thermocouple Measurement Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermocouples
- Thermocouple Sensor: Disadvantages
- Thermocouple Sensor: Choosing the Right Thermocouple For Your Application
- How to Use a Thermocouple with Arduino?
- Thermocouple Sensor: Grove – High-Temperature Sensor
- Thermocouple Amplifiers
- Summary
What is a Thermocouple Sensor?
A thermocouple is a sensor for measuring temperature, and it consists of two metal pieces welded together at one end. This welded end creates a reference junction for measuring the temperature. The thermocouple probe is frequent in multiple application areas due to its relatively affordable price, reliability, wide measurement range, and interchangeability.
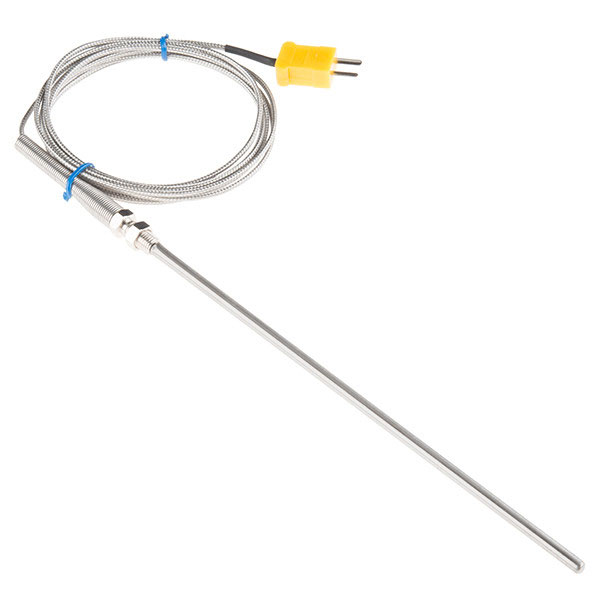

An industrial thermocouple sensor probe
Thermocouple Types
The following are the 12 types of thermocouples.
K type, J type, T type, E type, R type, S type
B type, N type, C type, M type, D type, G type
K, J, N, T, M, and E types fall under the nickel-alloy (Base Metal) category. On the other hand, R, S, and B are known as Noble Metal (platinum/rhodium-alloy) thermocouples. The last set (C, D, and G types) contain tungsten/rhenium alloys, but the most popular type among them is the K-type thermocouple.
How Does A Thermocouple Work?
A thermocouple operates based on the Seebeck or thermoelectric effect, discovered by German physicist Thomas Johann Seebeck in the 18th century. This effect states that two different metals generate an EMF (ElectroMotive Force) at their point of contact (welded junction) when subjected to temperature changes. Also, the metals produce this voltage potential passively without requiring a signal conditioner.
The hot junction results from the heat source, creating a temperature difference (voltage potential) between metal A and B. After that, thermocouple reference tables provide the voltage to temperature conversion to provide a temperature reading.
Special Offer: Get $200 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Temperature Sensors Comparison: Thermocouples, RTDs, and Thermistors
The following compares thermocouples, RTDs, and thermistors, the most commonly used temperature sensors.
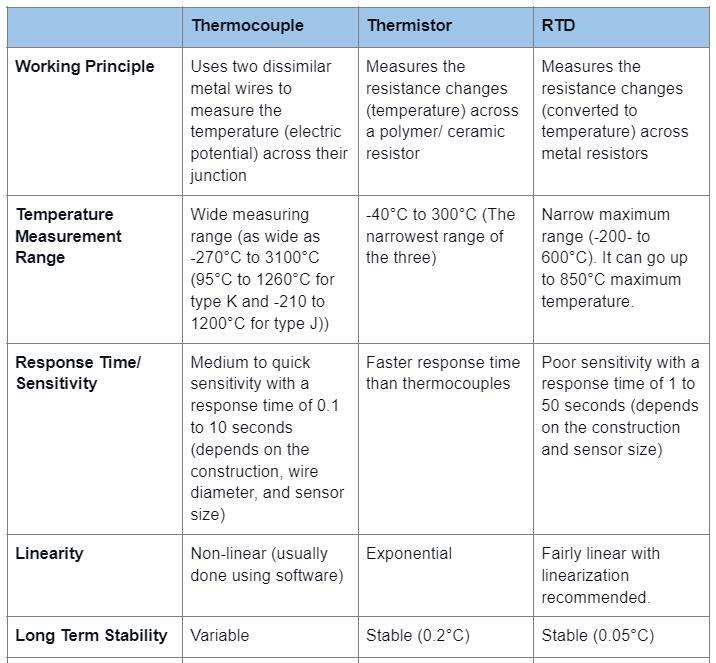
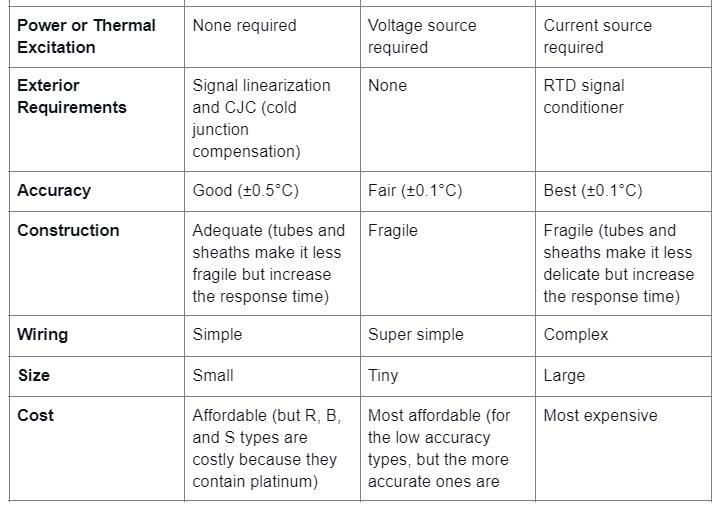
Thermocouple vs. Thermopile
Compared to a thermopile, a thermocouple measures temperature changes. But a thermopile converts thermal energy into electrical energy. Also, a thermopile consists of several thermocouples connected in series or parallel.
Thermocouple Measurement Applications

Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermocouples

Thermocouple Sensor: Disadvantages
- First, Not as accurate and stable as RTDs
- Second, Requires CJC (Cold Junction Compensation)
- Third, the Probability of noise in the low voltage outputs
Linearization required (for the sensor outputs)
Thermocouple Sensor: Choosing the Right Thermocouple For Your Application
Since there are different thermocouple sensor types, you need to consider the following factors before choosing one.

How to Use a Thermocouple with Arduino?
Whichever type of thermocouple you pick for your project, you can interface it with Arduino effortlessly. The following are a few project recommendations to help you get started.
Thermocouple Sensor: Grove – High-Temperature Sensor
This project requires a type K thermocouple plus a thermistor to detect the ambient temperature for compensation purposes. Using the Grove system and a dedicated grove port on the K-type thermocouple makes it easy to assemble the system via plug-n-play.
Thermocouple Amplifiers
Alternatively, you can try out the thermocouple amplifier. You will need a MAX31850K, a 64-bit ROM, 1-wire interface thermocouple to digital converter specifically built for the K-type thermocouple sensor. It allows several probes to connect to one microcontroller.
However, the MCP9600, a fully integrated EMF to temperature (°C) converter, is a superior alternative to the MAX31850K. Despite using the same I2C interface, it delivers a higher resolution, making it better. But you'll also need the K-type thermocouple sensor for this project.
Summary
In conclusion, thermocouple probes are the most popular sensor types for temperature measurement due to several reasons. But since they are available in multiple varieties, you need to pick the right one for your project. After going through this article, you should be in a better position to choose the best one, and if you have any questions, contact us for further clarification.
Special Offer: Get $200 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!