Changes to company policies, data protection laws, and cyberattacks have led to greater advancement in security systems. And one such system is biometric authentication technology such as Finger Sensors.
But first, today’s article looks at fingerprint sensors, types, construction forms, and applications. Read on.
Contents
What Is a Finger Sensor?
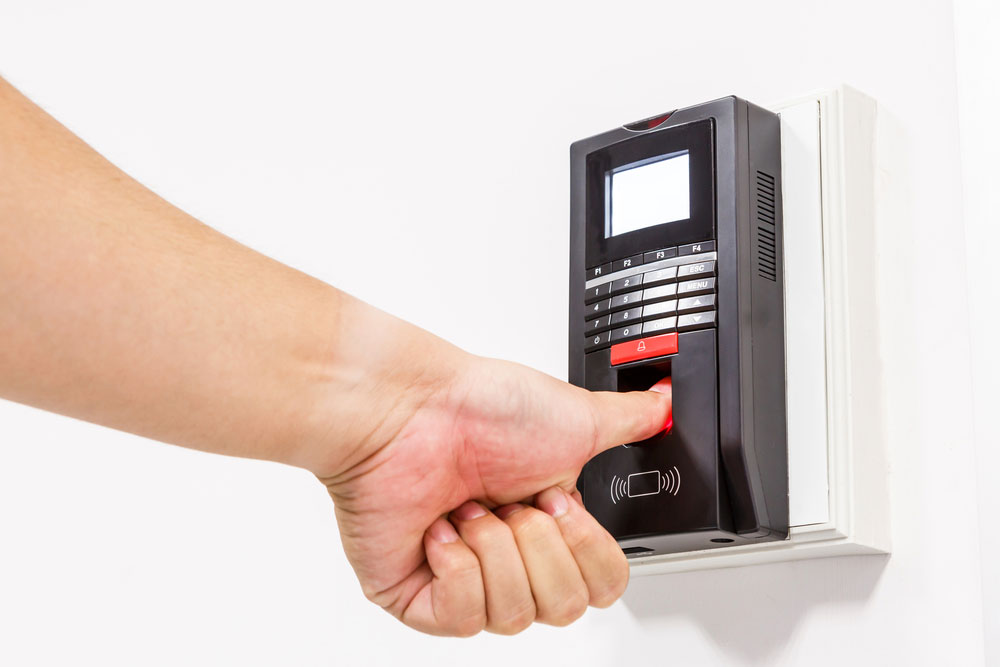

Fig 1: Fingerprint Scan for Unlock Door Security System
A fingerprint sensor or scanner is a biometric technology that identifies and authenticates an individual’s fingerprint. It then compares it to fingerprints stored in a database to grant entry if they match. Also, it blocks access if they don’t match.
Types of the Finger Sensors
The essential operation of all fingerprint sensors is obtaining an image of an individual’s fingerprint. It then runs through its database for a match.
Here’s a look at four types of fingerprint sensors.
Optical Scanners
These sensors take a visual image or photocopy of the finger using a digital camera. They’ll often illuminate the finger to obtain a better contrast of lines. At the same time, the light-sensitive microchip or image sensor records the data to generate a digital image.
Capacitive or CMOS Scanners
CMOS scanners use electricity to obtain fingerprint patterns. They have a touch-capacitive surface that detects ridges through a change in capacitance. Furthermore, it detects fingerprint valleys as they’ll produce no change in charge.
Ultrasonic Fingerprint Scanners
Ultrasonic sensors rely on the sending and reception of sound waves. Ridges and valleys reflect sound differently, allowing the ultrasonic sensors to create a 3D image of your fingerprint.
Thermal Scanners
Thermal sensors rely on the temperature difference between the contact (ridge) and non-contact (valley) points of your fingerprint.
Special Offer: Get $200 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!
Finger Sensor Construction Forms
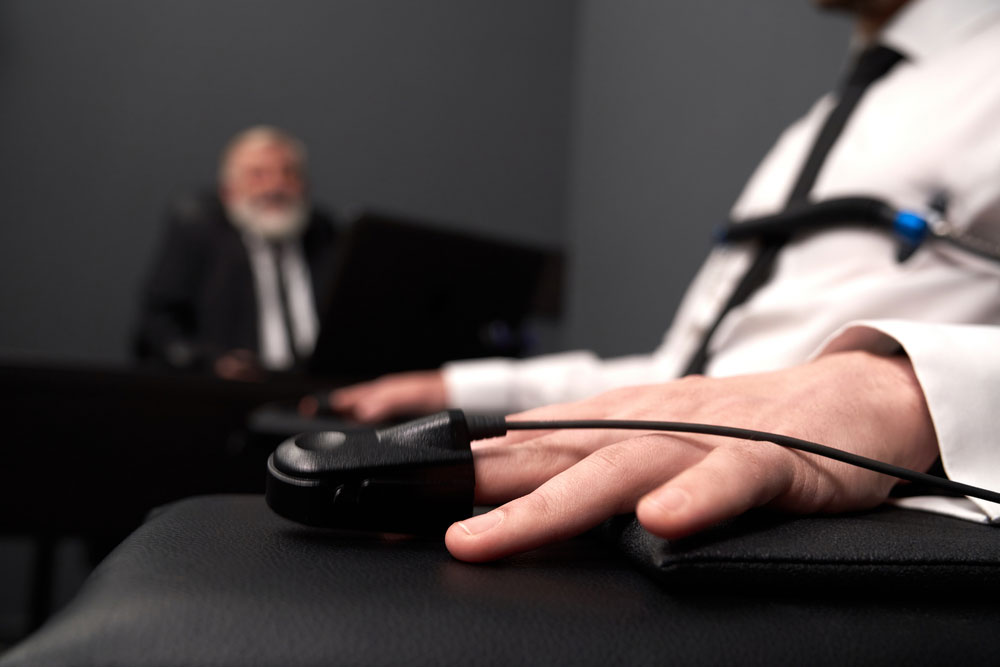

Fig 3: Close Up of Finger Sensor of Polygraph on Male Finger
Here are two fingerprint sensor construction forms.
Stagnant
In the stagnant form, you drag your finger across the small sensor scanning area. It’s cheaper, captures less ideal images, and is unreliable compared to the moving form.
Moving
You place your finger on the scanning area as the scanner runs underneath in the moving form. And it captures superior images since the scanner moves across at a constant speed.
Application of Finger Sensors
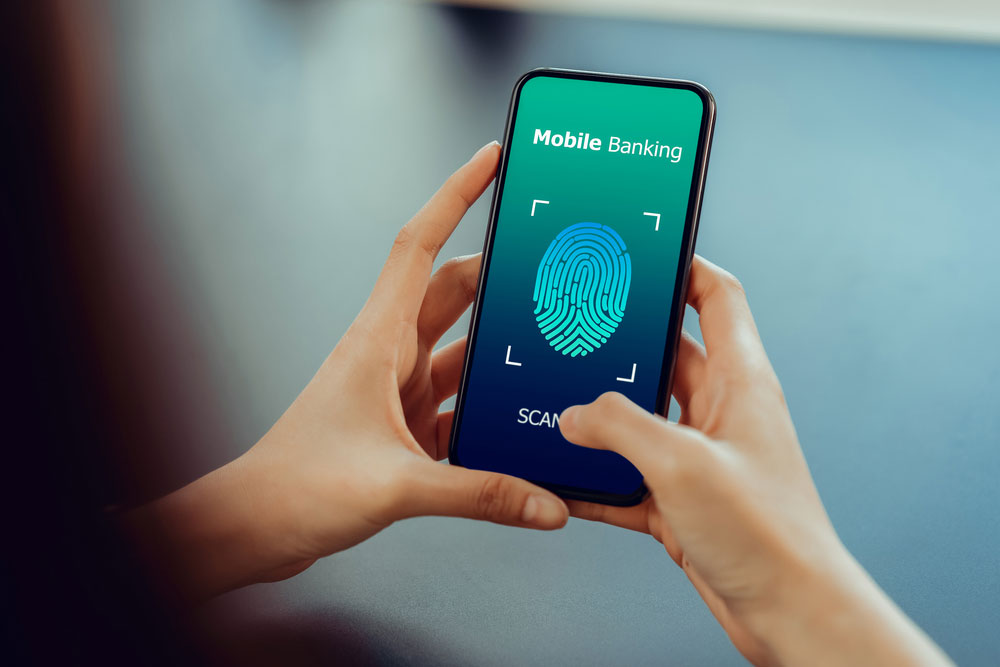

Fig 4: Hands Show the Fingerprint Scanner Screen to Access Online Banking
- Mobile phone security.
- Personal computer (PC) security.
- Biometric door locks.
- The Biometric car starter kits.
- Biometric safe locks.
- Lastly, in paid entrances to combat ticket fraud.
How Does a Fingerprint Scanner Work with Remote Access?
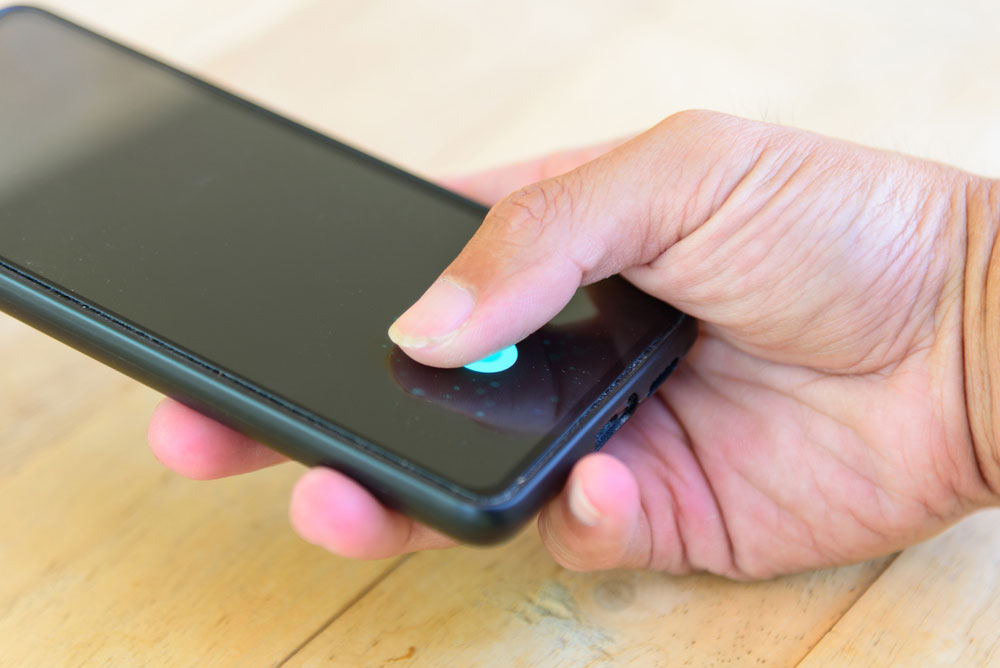

Fig 5: Fingerprint Scanner on Mobile Phone Screen
There are scenarios whereby your fingerprint sensor fails to detect and identify your finger. It may be due to a glitch, or your hands are wet.
Consequently, manufacturers anticipate such scenarios and give you alternative access to your destination or device.
However, there are times when you forget your device’s code and can’t unlock it by pin codes, passwords, or patterns. Therefore, the only option for Android and iOS devices is to reset the lock screen pins and passwords remotely.
You’ll only need to log in to a remote server and scan your fingerprints locally. The biometrics will then automatically transfer the data to the server. It’ll unlock your device if it gets that your fingerprint matches those in the database.
Conclusion
Fingerprint sensors are fast, have higher accuracy, improved security, and greater convenience. Also, you can design one to find your security needs.
And, if you’re planning on using a fingerprint sensor in your project and need assistance, contact us.
Special Offer: Get $200 off your order!
Email [email protected] to get started!